![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osteology of Rotator Cuff
|
The rotator cuff is made up of the scapula and the clavicle bones
|
|
|
Ligaments of Scapula
|
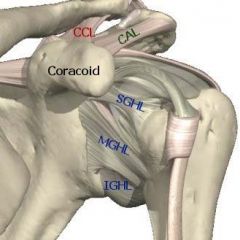
Coracoclavicular (CCL, 2) - trapezoid and conoid
Coracoacromial (CAL) Superior Glenohumeral (SGHL) Middle Glenohumeral (MGHL) Inferior Glenohumeral (IGHL) |
|
|
Acromioclavicular Joint
|
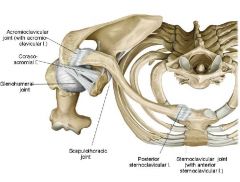
Ligament: acromio clavicular ligament
Function: uses this ligament to attach acromion and clavicle |
|
|
Coracoacromial Joint
|
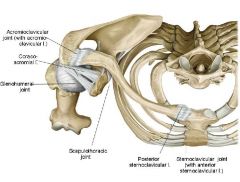
Uses corocoacromial Ligament to connect the coracoid and acromion processes
|
|
|
Posterior sternoclavicular Joint
|
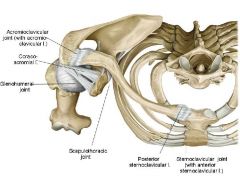
Uses posterior steroclavicular ligament to connect the clavicle to the manubrium. It also uses the Anterior sternoclavicular Ligament on the front side.
|
|
|
Saddle Joint of clavicle to manubrium
|
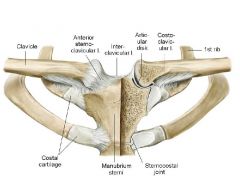
Uses the costoclavicular ligament deep to the anteriorsternoclavicular ligament in order to connect some of the clavicle to the cartilaginous areas of the manubrium
|
|
|
Scapulothoracic Articulation/Scapulothoracic Joint
|
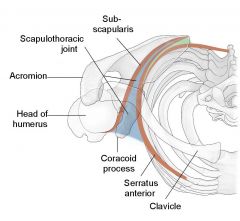
Only has soft tissue:
Joint is surrounded by Subscapularis on Posterior side of joint and surrounded by serratus anterior on the anterior side of joint. |
|
|
Superficial Hypaxial Muscles of Back Region
|
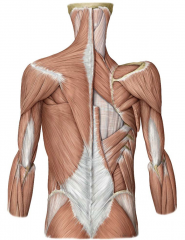
Five Muscles:
Layer 1 : trapezius and latissimus dorsi Layer 2 : levator scapulae, rhomboid minor, rhomboid major ALL INNERVATED BY BP EXCEPT TRAPEZIUS (innervated by accessory nerve CNXI) |
|
|
Hypaxial innervation
|
All innervated by the ventral rami of spinal nerves
|
|
|
epaxial innervation
|
All innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves
|
|
|
Trapezius Muscle
|
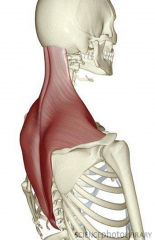
Diamond Shape muscle, most superior and most superficial muscle of the back
PA:external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, spinous processes of C7-T12 DA: Lateral 1/3 of clavicle (anteriorly), acromion, and spine of scapula Action: elevates, depresses, retracts the scapula; rotates glenoid fossa superiorly or upwards BS: Transverse Cervical Artery: (superficial branch of transverse cervical artery: superficial cervical artery) Motor innervation: Cranial Accessory Nerve XI Sensory Innervation/proprioception: Spinal Nerves C3 and C4 TCART-trapezius has tranverse cerv art, |
|
|
Triangle of Auscultation
|
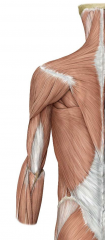
Posterior side:
Borders: Trapezius medially, Deltoid superiorly, latissimus dorsi inferiorly |
|
|
Lumbar Triangle/Inferior Lumbar triangle/Triangle of Petit
|
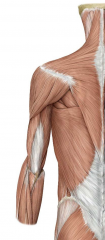
Slight weakening in lateral abdominal wall which is prone to herniation. Sits laterally to the portion of the latissimus dorsi which is tendonous
|
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
|
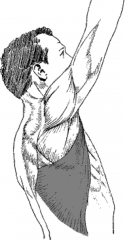
muscle that sits slightly deep to the trapezius
PA: Spinous Processes of T7-T12 (inferior six SP of T vert), thoracolumbar fascia, illiac crest, and inferior 3 ribs. DA: Floor of intertubercular groove of humerus Action: extends, adducts, and medially rotates humerus; raises torso towards arms during climbing; pulls humerus down when torso is fixed BS: Thoracodorsal Artery Innervation: Thoracodorsal nerve C6 C7 C8 LATD: TD artery/TD nerve C6C7C8 Pull ups are great! |
|
|
Deeper Posterior Axioappendicular Muscles
|
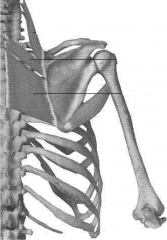
Levator Scapulae, Rhomboid Major, Rhomboid Minor
These are all still hypaxial muscles |
|
|
Rhomboid Major Muscle
|
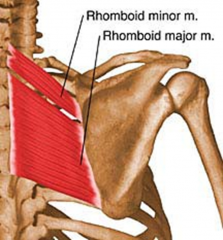
Sits on the most inferior portion of scapula under minor and levator
PA:Spinous Process of T2-T5 DA: Medial Border of scapula from Spine to Inferior Angle Action: Retract, elevate, rotate scapula downward and fix scapula to the thoracic wall BS: Dorsal Scapular Artery Innervation: Dorsal Scapular Nerve C4 and C5 |
|
|
Rhomboid Minor Muscle
|
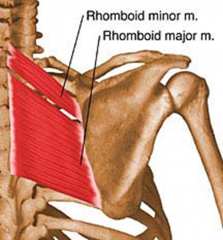
Sits superior to the Rhomboid major Muscle
PA: Nuchal Ligament, Spinous processes of C7 and T1 DA: Medial end of spine of scapula Action: Retract, Elevate, Rotate scapula downwards and and scapula to thoracic wall BS:Dorsal Scapular Artery Innervation: Dorsal Scapular Nerve C4 and C5 |
|
|
Levator Scapulae
|
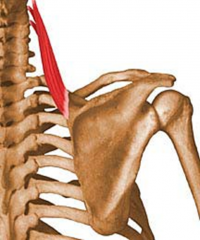
Superior to the Rhomboid Muscles
PA: posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1-C4 DA: Medial border of scapula at the superior portion of the scapular spine Action: elevates scapula, tilts glenoid cavity inferiorly BS: Dorsal Scapular Artery Innervation: Dorsal Scapular Nerve C5 and Cervical Spinal Nerves C3 and C4 DSN 5 Raise your scapula to the sky |
|
|
Circulation of Back, Shoulder, and Pectoral Regions
|
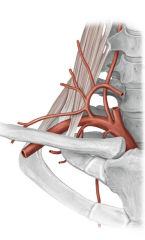
There are two major arteries that accomplish this:
Subclavian Artery and Axillary Artery |
|
|
Subclavian Artery Origin on Left and Right
|
Asymmetric Artery:
Origin on right side is brachiocephalic trunk and origin on left side is the aortic arch. Arises posterior to sternoclavicular joint and right lateral to manubrium. Divided into three divisions: Part one is anteior to scalene muscle, part two is posterior to scalene muscle, and part three is lateral to scalene muscle. After it passes the clavicle, it becomes the axillary artery |
|
|
Subclavian Artery Divsions of Medial portion of Subclavian Artery
|
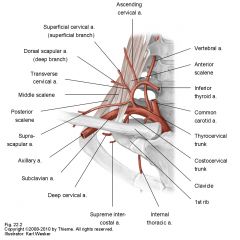
Internal thoracic (mammary)-goes inwards and anteriorly
Vertebral Artery- goes up through the transverse foramina of C spine and is important for brain blood carriage Thyrocervical trunk-runs into thoracic cavity and lies at the posterior aspect of the thoracic wall, lateral to sternum. Is important for recirculation or anastomosis during coronary bypasses. |
|
|
Transverse Cervical Artery of the Thyrocervical Arterial Trunk
|
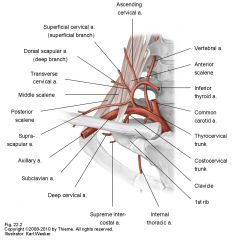
Arises from Medial Branch of subclavian artery
Splits into superficial branch and deep branch: superficial cervical artery and dorsal scapular artery |
|
|
Thryocervical Arterial Trunk
|
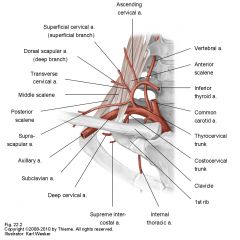
Splits into:
transverse cervical artery suprascapular artery |
|
|
Suprascapular Artery
|
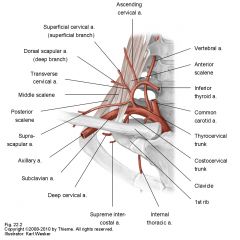
Goes to the suprascapular fossa and the suprascapular region.
|
|
|
Subclavian Artery Division at the Posterior aspect of the subclavian artery
|
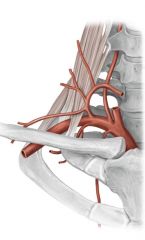
Becomes the Costocervical Arterial Trunk:
composed of Supreme Intercostal Artery and Deep Cervical Artery |
|
|
Deep cervical artery
|
will go deep into the neck structure
|
|
|
supreme intercostal artery
|
Follows under the clavicle and first rib
|
|
|
Lateral Part of Subclavian Artery
|
Has NO branches.
At times, the dorsal scapular artery may arise independent from this part of the subclavian artery The lateral border of first rib is where this part of the subclavian artery becomes the AXILLARY artery |
|
|
Subscapular artery
|
Arises from Axillary artery from subclavian artery
|
|
|
Thoracodoral artery
|
Arises from the subscapular artery from axillary artery
|
|
|
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN AXILLARY ARTERY IS BLOCKED?
|
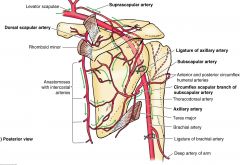
Blood flow still remains because the circumflex scapular branch of subscapular artery becomes reversed to allow blood to flow to the distal portion of the axillary artery and also via deep brachial artery
|

