![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the normal range for potassium level?
|
3.5–5.0 mEq/L
|
|
|
What are the surgical causes of hyperkalemia?
|
Iatrogenic overdose, blood transfusion, renal failure, diuretics, acidosis, tissue destruction (injury/hemolysis)
|
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hyperkalemia?
|
Decreased deep tendon reflex (DTR) or areflexia, weakness, paraesthesia, paralysis, respiratory failure
|
|
|
What are the EKG findings of hyperkalemia?
|
Peaked T waves, depressed ST segment, prolonged PR, wide QRS, bradycardia, ventricular fibrillation
|
|
|
What are the critical values of hyperkalemia?
|
K+ > 6.5
|
|
|
What is the urgent treatment of hyperkalemia?
|
IV calcium (cardioprotective), EKG monitoring
Sodium bicarbonate IV (alkalosis drives K+ intracellularly) Glucose and insulin Albuterol Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) and furosemide (Lasix) Dialysis |
|
|
What is the nonacute treatment of hyperkalemia?
|
Furosemide (Lasix), sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate)
|
|
|
What is the acronym for the treatment of acute symptomatic hyperkalemia?
|
"CB DIAL K+":
Calcium Bicarbonate Dialysis Insulin/dextrose Albuterol Lasix Kayexalate |
|
|
What is "pseudohyperkalemia"?
|
Spurious hyperkalemia as a result of falsely elevated K+ in sample from sample hemolysis
|
|
|
What acid-base change lowers the serum potassium?
|
Alkalosis (thus, give bicarbonate for hyperkalemia)
|
|
|
What nebulizer treatment can help lower K+ level?
|
Albuterol
|
|
|
What are the surgical causes of hypokalemia?
|
Diuretics, certain antibiotics, steroids, alkalosis, diarrhea, intestinal fistulae, NG aspiration, vomiting, insulin, insufficient supplementation, amphotericin
|
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hypokalemia?
|
Weakness, tetany, nausea, vomiting, ileus, paraesthesia
|
|
|
What are the EKG findings of hypokalemia?
|
Flattening of T waves, U waves, ST segment depression, PAC, PVC, atrial fibrillation
|
|
|
What is a U wave?
|
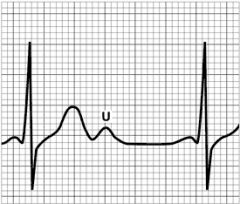
U wave
|
|
|
What is the rapid treatment for hypokalemia?
|
KCl IV
|
|
|
What is the maximum amount of potassium that can be given through a peripheral IV?
|
10 mEq/hour
|
|
|
What is the maximum amount of potassium that can be given through a central line?
|
20 mEq/hour
|
|
|
What is the chronic treatment for hypokalemia?
|
KCl PO
|
|
|
What is the most common electrolyte-mediated ileus in the surgical patient?
|
Hypokalemia
|
|
|
What electrolyte condition exacerbates digitalis toxicity?
|
Hypokalemia
|
|
|
What is the normal range for sodium level?
|
135–145 mEq/L
|
|
|
What are the surgical causes of hypernatremia?
|
Inadequate hydration, diabetes insipidus, diuresis, vomiting, diarrhea, diaphoresis, tachypnea, iatrogenic (e.g., TPN)
|
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hypernatremia?
|
Seizures, confusion, stupor, pulmonary or peripheral edema, tremors, respiratory paralysis
|
|
|
What is the usual treatment supplementation slowly over days for hypernatremia?
|
1/4 NS or 1/2 NS
|
|
|
What are the surgical causes of hypovolemic hyponatremia?
|
Diuretic excess, hypoaldosteronism, vomiting, NG suction, burns, pancreatitis, diaphoresis
|
|
|
What are the surgical causes of euvolemic hyponatremia?
|
SIADH, CNS abnormalities, drugs
|
|
|
What are the surgical causes of hypervolemic hyponatremia?
|
Renal failure, CHF, liver failure (cirrhosis), iatrogenic fluid overload (dilutional)
|
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hyponatremia?
|
Seizures, coma, nausea, vomiting, ileus, lethargy, confusion, weakness
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hypovolemic hyponatremia?
|
NS IV, correct underlying cause
|
|
|
What is the treatment for euvolemic hyponatremia?
|
SIADH: furosemide and NS acutely, fluid restriction
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hypervolemic hyponatremia?
|
Dilutional: fluid restriction and diuretics
|
|
|
What may occur if you correct hyponatremia too quickly?
|
Central pontine myelinolysis!
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of mild postoperative hyponatremia?
|
Fluid overload
|
|
|
How do you remember the sodium level in S.I.A.D.H.?
|
S.I.A.D.H. = Sodium Is Always Down Here.
|
|
|
What is pseudohyponatremia?
|
Spurious lab value of hyponatremia as a result of hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, or hyperproteinemia
|

