![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
162 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where to find RNZAF Specific directions in T6 Flight manual?
|
Supplements
|
|
|
Whose responsibility to report errors in flight manual?
|
Everyone |
|
|
Difference between flight manual and pilots checklist
|
Flight manual contains itemised procedures with amplification. Checklist contains itemised procedures without amplification.
|
|
|
3 reasons for aircraft limitations
|
Prevent damage, identify correct equipment operation, and safe aircraft operation |
|
|
Difference between warning, caution and note
|
Warning is life threatening or injury, caution is damage to equipment, and note is an operating procedure which is essential to emphasise |
|
|
Three danger areas around T6
|
Prop, prop wash, exhaust
|
|
|
Four purposes of aircraft fuselage
|
Support crew and pax and cargo, support wings and empennage, support engines, support landing gear, provide a pressurised cell
|
|
|
What is tension?
|
The stress that resists a force that tends to pull something apart.
|
|
|
What is a force comprising of tension and compression?
|
Bending |
|
|
What is shear?
|
The stress that resists the force tending to cause one layer of material to slide over an adjacent layer.
|
|
|
What is torsion?
|
The stress that produces twisting.
|
|
|
Six Properties of metal |
Hardness, strength, malleability, density, conductivity, elasticity, thermal expansion |
|
|
Three kinds of A/C structure
|
Truss, Monocoque, Semi-Monocoque |
|
|
Five primary structural members of semi-monocoque
|
Frame, Bulkhead, Skin, Stringer, Longeron |
|
|
What is a Bulkhead?
|
A fuselage component that has no central aperture that distributes loads to other load bearing members
|
|
|
What is a Longeron? |
Longitudinal structure member that extends across several frame members and helps the skin support primary bending loads
|
|
|
What is the Skin? |
Carries the shear loads from pressurisation and fuselage twisting. Transfers to longerons, stringers and other components
|
|
|
Four purposes of the wings |
Create lift, store fuel, support landing gear, store accessories (Fuel tanks, Bombs etc) |
|
|
Four wing structural components |
Ribs, Spar, Skin, Bulkhead, Stringer |
|
|
Three basic types of wing structure |
Cantilever, semi-cantilever, externally braced |
|
|
What are the structural components of the wing? |
Spar, stringer, ribs, truss braces, bulkheads, skin |
|
|
Purpose of A/C transparency |
Satisfies various visibility requirements for Crew and Pax whilst maintaining structural strength |
|
|
Materials that make up composite structure
|
Fibre and Glue/Epoxy |
|
|
Types of composite structure
|
Monolithic and Sandwich |
|
|
Types of reinforcements for composites
|
Carbon Fibre, Fiberglass, and Kevlar (Aramid) |
|
|
Five secondary flight controls
|
Flaps, Spoilers, Speedbrake, Trim, Slats, Slots |
|
|
What is the purpose of flaps?
|
To augment lift so that the A/C can fly at lower speeds |
|
|
What are leading edge lift augmentation devices?
|
Slats, Slots, and Kruger Flaps (Leading edge flaps)
|
|
|
What is a speedbrake?
|
Increase in drag with no increase in lift |
|
|
What is a ground spoiler? |
Dumps as much lift to increase brake effectiveness. |
|
|
Three types of trim tab
|
Servo, Balance, Spring, and Ground Adjustable |
|
|
What is servo assisted trim tab? |
Utilises airflow over the aerofoil to assist in control surface deflection |
|
|
Disadvantages of powered flight controls
|
Requires redundancy incase of power failure, no feel or synthetic feel
|
|
|
Components of basic flight control system |
Bell Crank, Push rods, Control Column, Cable, Pulley, Torque Tube |
|
|
What is a Bell Crank |
Changes the direction of motion through an angle
|
|
|
What is a fairlead?
|
An eyelet that keeps cables inline |
|
|
Control Harmony Ratio |
1:2:4 (Aileron, Elevator, Rudder) |
|
|
Four main types of turbines |
Turbojet, Turbofan, Turboprop, and Turboshaft |
|
|
Advantages of gas turbine engine
|
Less moving parts Efficient at high altitudes Less vibration |
|
|
Components of gas turbine engine
|
Intake, Compressor, Combustion chamber, turbine, and exhaust |
|
|
Types of compressor
|
Axial and centrifugal |
|
|
Advantages of centrifugal compressor
|
15:1 Compression Ratio (High) Low cost Low weight High efficiency over wide range of RPM Allows for a short engine Simple to manufacture |
|
|
Disadvantages of centrifugal compressor
|
High frontal area/Increased drag |
|
|
Advantages of axial compressor |
Small frontal area/Less drag Constant velocity throughout the compressor |
|
|
Disadvantages of axial compressor |
Expensive Difficult to manufacture Low compression ratio (1.25:1) Long engine |
|
|
Describe operation of an axial compressor
|
Air is sped up through the rotors, it is then dispersed through the stators where the speed decreases but the pressure increases. Over multiple stages, the pressure increases to point sufficient for combustion. |
|
|
Purpose of combustion chamber
|
To ignite the fuel air mixture
|
|
|
Difference between single/multiple spool compressor
|
Single stage- Rear operates at a fraction of the capacity and the front is overloaded. No good for abrupt control input changes Multiple stage- Each spool sets its own operating speed. Much more efficient and can react to control input changes. |
|
|
Three kinds of combustion chamber
|
Annular, Cananular, Multiple Chamber |
|
|
Purpose of fuel nozzle
|
Introduces atomised and vaporised fuel |
|
|
Purpose of turbines
|
Transform kinetic energy into mechanical energy. Turning props etc |
|
|
Three components turbines drive |
|
|
|
What is a free power turbine? |
Separate shafts powering compressor and propeller |
|
|
Six kinds of gas turbine accessories
|
Oil Pump Hydraulic pump FCU Starter Generator Gauges (Tachometer etc) |
|
|
Purpose of a fuel control unit
|
To control the amount of fuel to the engine |
|
|
Six engine monitoring systems
|
Turbine temp, Torque, thrust, compressor speed, oil pressure, oil temp, fuel flow, EPR |
|
|
Advantages of a tractor propeller
|
Provides more slipstream over the aerofoil
|
|
|
What is a fixed pitch prop?
|
Maintains a pitch manufactured to a certain purpose of the A/C. 3 types: Climb, all purpose, cruise
|
|
|
Types of props:
|
Ground adjustable Constant speed variable pitch |
|
|
Purpose of feathering prop |
Reduces drag on a non running engine. Can be used during engine shutdown and failed engine |
|
|
Four materials for propeller construction
|
Wood, aluminium , steel, composite |
|
|
Two advantages of wood props:
|
|
|
|
Disadv of wooden props:
|
Susceptible to damage, used for low HP engines |
|
|
Adv of aluminium props:
|
Light, Strong, Machinable, requires less maintenance, long service life |
|
|
Disadv of aluminium props:
|
Susceptible to corrosion, damage must be removed |
|
|
Advantages of composite props:
|
Lightweight, durable, can be formed in complex shapes, absorbs vibration, resistant to corrosion, ease of repair |
|
|
Disadv of composite props: |
Expensive, susceptible to ground debris |
|
|
What is a hub? |
Holds the blades of a prop. Provides mount for piston and dome. Made of steel and aluminium |
|
|
Describe the effect of engine shut down on feathering propeller with counterweights
|
Fluid drains Prop coarsens to feathered due to CTM and position of counterweights |
|
|
Three purposes of a governor |
Controls oil amount to piston Senses engine rotational speed |
|
|
Describe the operation of a governor in an over speed condition? |
Flyweights move outwards Pilot valve moves up Fluid drains Prop coarsens |
|
|
Purpose of speeder spring
|
Adjusts the pressure exerted on the flyweight and pilot valve. |
|
|
Four components of a prop governor
|
Pump, pilot valve, speeder spring, flyweights |
|
|
Purpose of oil system |
To deliver oil to internal engine components so as to reduce friction between moving parts |
|
|
Four secondary purposes of an oil system
|
Cleans, Removes heat, seals between moving parts, cushioning between metal parts, protects against corrosion, provides hydraulic power |
|
|
What is viscosity? |
|
|
|
What is cloud point? |
Point at which the fluid starts to solidify and create a cloudy solution |
|
|
Specific Gravity |
Weight of fluid compared to water
|
|
|
What is flash point? |
Point at which oils emit ignitable vapour |
|
|
Three methods of lubrication
|
Pressure, Splash, Spray |
|
|
What is a dry sump? |
Oil is stored in its own separate reservoir. |
|
|
What is a scavenge pump? |
Pump that returns oil back to reservoir
|
|
|
Purpose of a pressure regulator |
Removes excess pressure after oil is passed through pressure pump
|
|
|
Purpose of check valve
|
To control one way flow |
|
|
Purpose of vent |
To eliminate pressure changes in reservoir. Breather hole |
|
|
What can happen if fuel is too volatile?
|
Causes vapour lock where a blockage is created in the system. |
|
|
What is fuels flashpoint?
|
The temp at which a fuel will ignite |
|
|
Why is fuel measured in weight rather than volume? |
Size and volume changes in flight due to temperature and altitude but weight remains the same |
|
|
Preferred fuel in RNZAF |
F34 FSII |
|
|
Where do you find approved alternate fuel for the A/C |
Flight Manual |
|
|
Three contaminants found in fuel |
Microbial growth Particulate matter |
|
|
Why is it necessary to drain a portion of the fuel for daily checks? |
To check for water |
|
|
What are the ways to heat fuel and why?
|
Bleed air and/or oil into heat exchanger to prevent ice crystals forming.
|
|
|
Component that indicates fuel consumption
|
Fuel flow meter |
|
|
Two sections of the fuel control unit |
Fuel metering section |
|
|
Draw and describe jet pump |
DESCRIBE and ADD Diagram !!! |
|
|
Components in a basic fuel system
|
Fuel tank Filter Fuel pump Booster pump Jet pump Strainers Dump pump Dipstick Drip stick Check valve Engine System Fuel drains Temp probes Fuel flow indicator |
|
|
Components of engine fuel system
|
High pressure pump Fuel filter Fuel heater Fuel flow meter Fuel control unit |
|
|
Uses of environmental air |
Air conditioning De-fogging Ventilation Pressurisation Supplemental oxygen Equipment cooling Anti-G |
|
|
What component cools bleed air out of the engine?
|
Heat exchanger |
|
|
What air is used to cool the bleed air in a heat exchanger?
|
Ram air |
|
|
Draw and describe the vapor cycle system
|
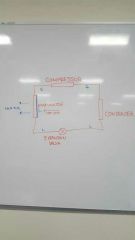
A simplified description required !!! |
|
|
Three main purposes of A/C pressurisation system? |
Maintain cabin pressure Prevent rapid changes in cabin altitude Provide reasonably fast exchange of air |
|
|
A/C pressurisation component that regulates cabin pressure? |
Outflow valve |
|
|
Component that ensures outside pressure is not greater? |
Safety valve |
|
|
Component that allows for thermal expansion
|
|
|
|
Describe the operation of a water separator |
Moves air in circular motion with sharp turns, heavy particles carry on to the collection chamber
|
|
|
Four kinds of supplemental oxygen
|
Gas Solid/chemical Mechanically |
|
|
Purpose of the G-suit |
Protect pilot from g-forces moving blood away from brain to feet and butt. |
|
|
Purpose of hydraulics |
Transferring energy from one area to another |
|
|
Three advantages of pneumatic system |
Fast Can be dumped easily to atmosphere Initial cost is less Less maintenance Better for long distances Sourced from bleed air |
|
|
Advantages of hydraulic system
|
High pressures Lift heavy loads Utilise engine power to produce pressure No energy loss due to pressurisation |
|
|
Disadvantages of Hydraulic |
Can be toxic Higher maintenance Shorter distances necessary Need a reservoir for returning fluid |
|
|
Disadvantages of pneumatic |
Generally only used for in/out applications Large pistons required for the same power due to air being compressible |
|
|
What is chemical stability
|
The ability of hydraulic fluid to resist oxidisation |
|
|
Properties of hydraulic fluid |
Chemical stability Flash point Fire point |
|
|
Difference between flash/fire point? |
Flash point is when it is at a temperature that it emits flammable vapour. Fire point is when the fluid can sustain a flame |
|
|
Three types of hydraulic fluid |
Vegetable Mineral Synthetic |
|
|
Purpose of pressure regulator valve in a hydraulic system |
To remove surplus pressure so the output is controlled |
|
|
Purposes of an accumulator
|
|
|
|
Describe the operation of an accumulator in a hydraulic system |
Compressed air/gas in one chamber holds pressure on hydraulic fluid in the other chamber which enables the fluid to be stored under pressure.
|
|
|
What is a check valve
|
One way valve to prevent reverse flow of a fluid |
|
|
Purposes of landing gear |
Shock absorber for landing Stable platform for the A/C on the ground |
|
|
Types of landing gear layout
|
Tricycle Tandem |
|
|
Advantages of tail dragger |
Cheaper |
|
|
Disadvantages of tail dragger
|
Prone to nose-over Steering is harder Loading cargo is not easy Prone to ground looping |
|
|
Advantages of tricycle undercarriage |
Good visibility Nose wheel can be augmented for steering Much easier ground handling Nose over and ground looping is reduced |
|
|
Why do you put landing gear pins in on the ground? |
To prevent accidental raising of Landing gear whilst on ground |
|
|
Part of the tyre which provides anchor to the wheel?
|
Bead |
|
|
Describe the A/C brake system |
Pistons clamp brake pads on to brake discs. Can be multiple discs and calipers. (same as car) |
|
|
Types of A/C steering
|
Nose wheel steering |
|
|
Main components of shock strut
|
Piston tube Gas Hydraulic fluid/oil Metering pin/orifice Torsional scissor link |
|
|
Briefly describe operation of shock strut |
The initial shock is absorbed by the nitrogen in the cylinder, and oil is then metered in to resist continuous bouncing. |
|
|
What provides emergency power systems
|
External ram air turbines APU |
|
|
What does a GPU provide?
|
Auxiliary power |
|
|
What is the reverse current cut out?
|
Disconnects battery from the generator when the generator output is lower than battery output
|
|
|
What is a bus bar?
|
Main distribution component to services |
|
|
Purpose of suppressor |
A capacitor to remove radio interference caused by commutation |
|
|
What are the three times main batteries are used? |
Before and during engine start Emergencies Post shutdown |
|
|
Three types of 24v DC batteries? |
Lead acid Nicad |
|
|
How many times can a circuit break be reset in flight |
Once |
|
|
What is the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker? |
Fuse needs to be replaced whilst circuit breaker can be reset |
|
|
Why is a bus distribution split into sections? |
For redundancy - so you can shed the non-essential loads. |
|
|
What is an APU
|
Auxiliary Power Unit - to provide electrical power, air pressure for starting main engines or both. |
|
|
Purpose of Ram air turbine?
|
To provide emergency power |
|
|
Issues of static build-up
|
Radio and radar interference |
|
|
What are static wicks
|
They discharge static electricity into the atmosphere |
|
|
What is the purpose of A/C bonding |
To create a single static charge across the airframe |
|
|
Methods of de-icing |
Thermal (hot air or electrical) Chemical |
|
|
Consequences of ice build up on A/C |
Drag increases Lift decreases Thrust decreases |
|
|
Two types of anti-icing |
Thermal (hot air or electrical) |
|
|
When do you use anti-icing
|
When knowingly flying into icing conditions |
|
|
Two sources of thermal anti-icing
|
Electrical |
|
|
Areas where electrical anti-icing is used
|
Leading edges Propellers Pitot tubes |
|
|
Operation of pneumatic de-icing
|
Pulsations of air into boot
|
|
|
What is scheduled servicing?
|
Servicing carried out on the A/C after a set period |
|
|
What is Out Of Phase Servicing |
Servicing that is not in line with A/C routine servicing
|
|
|
What is operational level maintenance
|
Flight line servicing for day to day A/C operations
|
|
|
Who is the technical Air Worthiness Advisor
|
C Eng
|
|
|
What is intermediate level maintenance |
Minor scheduled servicings carried out by both the SQN and various second line bays |
|
|
What is depot level maintenance
|
Major group servicings carried out by contractors such as Safe Air or Air NZ
|
|
|
What does the Maintenance Servicing Permit allow Pilots to conduct?
|
OLM - Operational Level Maintenance |

