![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
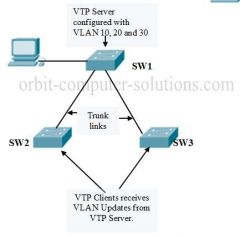
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) |
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that propagates the definition of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) on the whole local area network. To do this, VTP carries VLAN information to all the switches in a VTP domain. VTP advertisements can be sent over 802.1Q, and ISL trunks. |
|
|
IP Transit |
IP Transit is a service where an Internet Service Provider (ISP) allows traffic to travel through their network to its final destination |
|
|
Tier 1 provider |
Tier 1 providers have an expansive global reach. These providers peer with each other and act as the global conduit to all networks – thus forming the “backbone” of the Internet. |
|
|
MPLS |

Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) is a mechanism used within computer network infrastructures to speed up the time it takes a data packet to flow from one node to another |
|
|
VPLS |
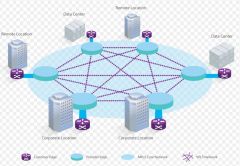
Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) is a way to provide Ethernet-based multipoint to multipoint communication over IP or MPLS networks. It allows geographically dispersed sites to share an Ethernet broadcast domain by connecting sites through pseudowires. |
|
|
SD-WAN |
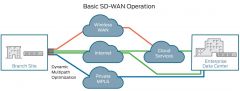
SD-WAN is an acronym for software-definednetworking in a wide area network (WAN). An SD-WAN simplifies the management and operation of aWAN by decoupling (separating) the networking hardware from its control mechanism. |
|
|
Wavelength |
G |
|
|
Fiber |

Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. |
|
|
Hosted PBS |
I |
|
|
Ethernet |
Ethernet is the technology that is most commonly used in wired local area networks (LANs). A LAN is a network of computers and other electronic devices that covers a small area such as a room, office, or building. |
|
|
Switch |

A switch, in the context of networking is a high-speed device that receives incoming data packets and redirects them to their destination on a local area network (LAN). |
|
|
Router |

A router is a device that analyzes the contents of data packets transmitted within a network or to another network. |
|
|
Burst Usage |
A specific amount of data sent or received in one intermittent operation. A burst operation implies that some threshold has been reached that triggers the burst. |
|
|
Aggregated Committed Data rate |
N |
|
|
Enterprise |
O |
|
|
Carrier |
P |
|
|
Outage |
Q |
|
|
Latency |
R |
|
|
Backbone |
B |
|
|
Peering connection |
T |
|
|
DIA Dedicated Internet Access |
U |
|
|
Off-net |
V |
|
|
On-net |
V |
|
|
SLA |
W |
|
|
Blackhaul |
A portion of the network that comprises the intermediate links between the core network, or backbone network, and the small subnetworks at the edge of the network. |
|
|
Milestone |
A significant event or stage in the life, progress, development, or the like of a person, nation, etc. == Contador, escalon (intermediate goal) |
|
|
RFO |
Reason for outage |

