![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Early toothdevelopment of structures come from __ and __ |
oral ectoderm ectomesenchyme (neural crest cells - originally ectoderm that migrate and become more like mesoderm) |
|
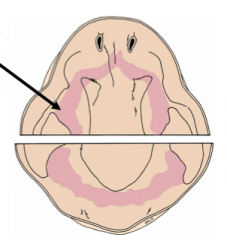
At 37 days, the Primary Epithelial band (pink) is present and gives rise to? In the initiation stage, the epithelial band forms from the thickening epithelium due to? |
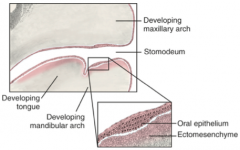
Dental lamina - tooth Vestibular lamina - between cheek and teeth Mitosis and change of orientation |
|
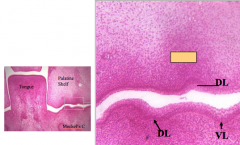
There is a change in size and thickness of the epithelial band (dental lamina) and an increase density of tissue under it which is the __ The above becomes? |
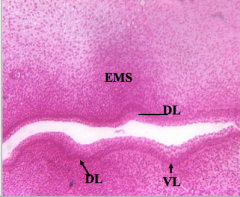
Ectomesenchyme (EMS) Becomes dental papilla |
|
|
The dental lamina gives rise to the dental placodes Certain factors cause thickening and direct mitosis: - What 2 stimulatory signals cause proliferation and differentiation of the dental lamina? -What inhibits it? |
- FGF (fibroblast growth factor) and WNT - BMP (bone morphogenic protein) |
|
|
Dental placode formations require Transcription factor p63 for? TNF (tumor necrosis factor) for? Also Ectodysplasin which is important in ectoderm/mesenchyme interactions - If there is a loss in this gene what results? -Over activation leads to? Sonic hedgehog is important as well |
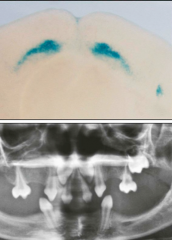
Mitosis Apoptosis, cell division, etch -Fewer teeth (hypodontia) -Extra teeth |
|
|
__ and __ directs the development early on __ is required for tooth development, this will change during development Later on __ takes over |

Neural crest and ectoderm (epithelium) Mandibular epithelium (ectoderm) Neural crest takes over |
|
|
The first arch expresses __ which induces Lhx-5 and Lhx-7 in ectomesenchyme very early in development -This is found in the ectoderm where teeth develop If this is introduced in the 2nd arch and not the first what happens? |
FGF8 FGF8 is down regulated and tooth placodes do not form (2nd arch is mostly for the external ear) |
|
|
FGF8 is found in the ectoderm where teeth develop FGF8 stimulates __ which is found in the ectomesenchyme where teeth develop BMP 2 and BMP 4 inhibit the above |
Pax 9 -Induction of ectomesenchyme by the ectoderm |
|
|
1st arch ectoderm influences the __ which goes back and influences the 1st arch ectoderm to become the tooth bud This develops into the? The ectomesenchyme develops into the? |
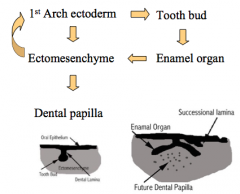
Ectomesenchyme Enamel organ Dental papilla |
|
|
1st arch ectoderm secretes __ to influence __ to release Lhx6, Lhx7, and Pax 9 which act on the 1st arch ectoderm to form the tooth bud - This happens under the influence of __ also and when __ is low If the above is not low, what occurs? |
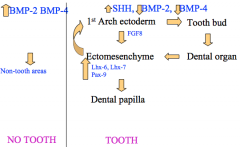
FGF8 to influence Ectomesenchyme -This happens under the influence of sonic hedgehog (SHH) also and when BMP2 and BMP4 is low If BMP2 and BMP4 are high no tooth develops |
|

|
- |
|
|
The __ invaginates and moves into the mesenchyme that is made up of? Bone formation also occurs, which is what type of bone formation? |
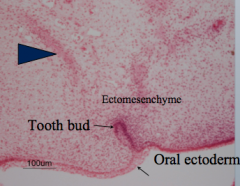
Oral Ectoderm, Neural crest cells Intramembranous bone formation (no cartilage matrix is needed, bone just forms) |
|
|
At week 8 in the bud stage there is cell proliferation of the tooth bud (ectoderm) after it invaginates inward What condenses around it? |
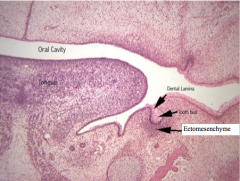
Ectomesenchyme (note Dental Lamina is oral ectoderm that invaginates inward to form the proliferating tooth bud) |
|
|
What stage is where the ectoderm has a significant effect on the underlying mesenchyme and directs the development of the tooth? |
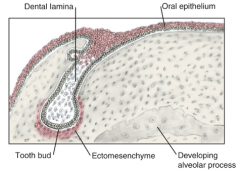
Bud stage |
|
|
At week 9-10 the invaginated ectoderm in the ectomesnchyme begin to surround the cells that will become the? The ectoderm appears as a __ |
Dental papilla Cap (hence Cap Stage) |
|
|
In order to go from the bud to cap stage, __ in mesenchyme is needed, if there is none, then teeth are arrested in bud stage Bmp4 in mesenchyme maintains BMP2 and SHH which is also needed for the cap stage for? Activin beta A and Pax 9 in mesenchyme are also needed to go to the cap stage |
Msx1 Epithelium proiferation |
|
|
Dental lamina ectoderm forms and attaches the? Below that is the? Outside of the above is the? What does the tooth germ include? Which arise from neural crest cells that give rise to ectomesenchyme? Which arise from oral ectoderm? |
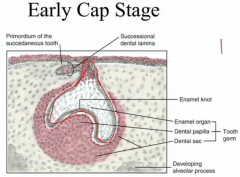
Enamel organ Dental papilla Dental Sac (dental follicle) Tooth germ: - Enamel organ - Dental papilla - Dental sac Neural crest (ectomesenchyme) - dental sac and dental papilla Enamel organ |
|
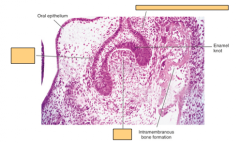
|
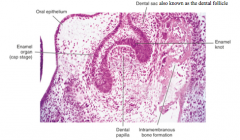
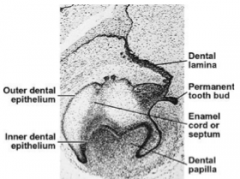
Cap stage sees formation of the dental organ (tooth germ) 1. Enamel organ 2. Dental papilla 3. Dental follicle |
|
|
Enamel organ is attached to the ectoderm by the? The enamel organ has what 3 things? |
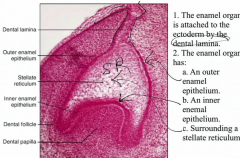
Dental lamina -Outer enamel epithelium -Inner enamel epithelium -Stellate Reticulum (surrounded by the inner) |
|
|
Within the enamel organ, what hydrophilic component accumulates to draw water in and form the stellate reticulum? |
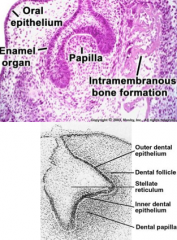
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) -Gives Stellate reticulum that appearance |
|
|
In the cap stage we have the -Enamel organ that eventually forms? -Dental papilla that eventually forms? -Dental sac that eventually forms? |
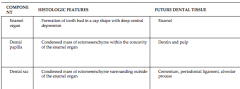
Enamel Dentin and pulp Cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar process |
|
|
What are clusters of non-dividing epithelial cells? -Its a signaling center that signals underlying ectomesenchyme -has expression of FGF4 and other genes Tooth shape is controlled by different concentration of signals - Early tooth development is directed by ectoderm. In later development what directs formation of each tooth type? |
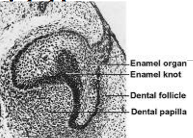
Enamel knot Factors in ectomesenchyme - Past the bud stage, the type of tooth that develops is dependent on ectomesenchyme and not the ectoderm |
|
Bell stage structures |
|
|
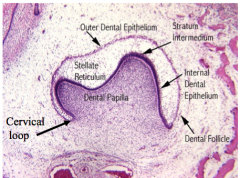
Bell Stage: Inner enamel epithelium (Internal dental epithelium) are __ cells with __ nuclei They become preameloblast epithelium with __ cells with nuclei where? Cells of inner dental papilla move up towards? |
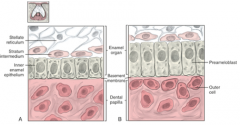
cuboidal, central nuclei columnar, nuclei closer to the stratum epithelium inner enamel epithelium |
|
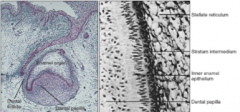
Early in the bell stage, the tooth germ maintains contact with ectoderm via? Enamel and dentin begin to form Inner enamel epithelium and stratum intermedium differentiate with different components |
dental lamina |
|
|
In the later stages, the dental and lateral lamina break up and what happens? The junction of the inner and outer enamel epithelium is the? |
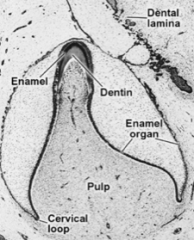
Tooth is no longer connected to oral epithelium -Fragmentation results in epithelial pearls (or eruption cysts) Cervical loop |
|
|
What is found between the outer dental epithelium and dental follicle and between the inner dental epithelium and dental papilla? -Shape of the tooth is the result of? |
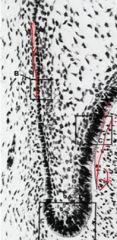
Basement membrane Different mitotic activity |
|
|
As the tooth moves through the bell stage it loses contact with the surface but reestablishes contact with the surface ectoderm forming the? |
Junctional epithelium |
|
|
Enamel, dentin, and cementum are secreted in what stage? Ectodermal tissue of the enamel organ and ectomesenchymal tissue of the dental papilla and dental sac interact to signal other layer to differentiate and begin secretion is what stage? The dental tissue fully mineralize at what stage? |
Apposition (secretory) stage Reciprocal induction Maturation stage |
|
|
Preameloblast of the inner enamel epithelium induce outer dental papilla cells to become? Preameloblast become polarized with the base of the cell located along? Apex is toward? |
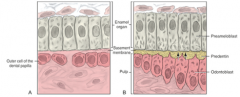
Odontoblasts The stratum intermedium Dental papilla |
|
|
Odontoblast are polarized in the __ direction of the ameloblast Nucleus is at the opposite end of the cell from the dentin Polarized odontoblasts secrete toward the preameloblasts -Odontoblast begin to secrete? |
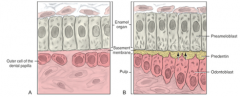
opposite Predentin |
|
|
After predentin is formed, what disintegrates? Preameloblast are induced to become presecretory then secretory ameloblasts that secrete? Lack of enamel or little enamel results in? Dentin displasia can result in? |
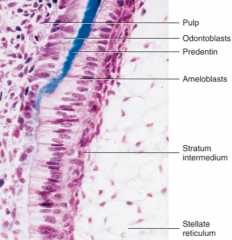
basement membrane between the preameloblast and odontoblast Enamel Amelogenesis imperfecta Dentinogenesis imperfecta |

