![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the androgen receptor blockers? |
Bicalutamide Enzalutamide Flutamide Niulatmide |
|
|
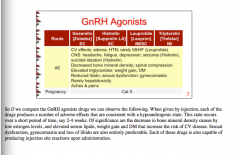
What are the GnRH agonists? |
Goserelin Histrelin Leuprolide Triptorelin |
|
|
What is a targeted alkylator? |
Estramustine |
|
|
What is the GnRH antagonist? |
Degarelix |
|
|
What is the 17-alpha inhibitor? |
Abiraterone |
|
|
What provides immunotherapy? |
Sipuleucel-T |
|
|
What is the most hormone sensitive of all cancers?
What are the two equivalent sources of androgens acting in the prostate?
What is the first line treatment of prostate cancer?
What are some non-drug approaches?
What is brachytherapy? |

|
|
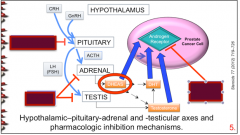
Where do GnRH agonists and antagonists act?
Where do CYP17A1 inhibitors act?
Where do the androgen receptor antagonists act?
Draw this out. |
|
|
|
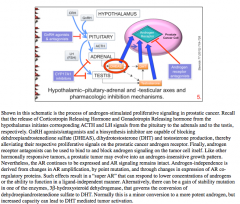
What does GnRH agonist treatment do? (think about the pulsatile secretion of GnRH)
What will this result in (flare up)? |

|
|
|
For the GnRH agonists, when given an injection, what are the adverse effects (think hypoandrogenic state)?
CV, CNS, bone mineral density, spinal, triglycerides, weight, DM, libido, sex, boobies, liver function, pain |
|
|
|
What is the GnRH receptor antagonist given by SC injection? What does it result in reduced levels of? How long does it take to castrate the testosterone?
What are some common AEs? Hypoandrogenic state + what two other effects? |

|
|
|
What does estramustine bind on prostate cancer? What is the result of this (mechanism)?
What are its effects comparable to?
What are some common AEs (think about estrogen)?
What will occur as a result of the elevated estradiol levels? |

|
|
|
What are the androgen receptor blocking drugs? They all produce AEs that are consistent with which states? Which one has CYP activity? Which one has some agonist and some antagonist activity? |

Bicalutamide = CYP activity |
|
|
Bicalutamide Enzalutamide Flutamide Nilutamide
Which one has HF/HTN Blood dyscrasias CNS effects GI toxicity, hot flashes, aches and pains, liver failure (BBW) Interstitial pneumonitis; respiratory insufficiency URTI Increased time to accommodate transition from light to dark Teratogens |

|
|
|
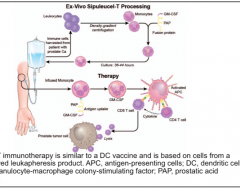
Which drug is autologous cellular immunotherapy designed to stimulate T-cell immunity against prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)?
Describe the process
What are some AEs? |

|
|
|
Here is the aforementioned process in figure format. By producing expression of the prostatic acid phosphatase on components of the immune system, the CD8+ T-cells (killer T-cells) are primed to seek out prostatic tumor cells anywhere in the body to erradicate them. |
|
|
What is the difference between a ketoconazole and a 17-alpha inhibitor?
Which state is produced by each? |
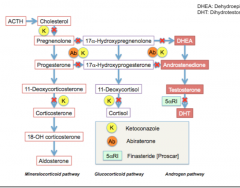
Ketoconazole => hypoaldosterone and hypocortisol state
17-alpha => hypermineralocorticoid state (prevents trantions of products from this pathway into other parallel pathways. |
|
|
Which CYP does abiraterone inhibit? What state is produced (BP, sodium, potassium levels)? What should you caution with? AE? Think liver and babies |

|
|
|
What is the pathway to testosterone?
How can testosterone be converted to estrone and estradiol? |

|
|
|
Does estrogen and androgen signaling have important in bone health in men? |
|
|
|
What were estrogens (estradiol, DES, estrone, ethinylestradiol) historically used for?
What do systemic high does of estrogen cause?
Do transdermal estrogens produce cardiovascular effects? |

|
|
|
What is testosterone converted to when it enters the target cell?
Is the off-label use of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors finasteride and dutasteride in an |

DHT = has a much longer ligand binding time on the androgen receptor than does testosterone. |
|
|
Does down regulation of AR activity necessarily correlate with drug ability to inhibit conversion of testosterone to DHT?
Can cellular location and enzyme expression levels predict the degree of testosterone metabolism to DHT?
Basically, are there off target effects of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors? |

|
|
|
Androgens are metabolized to estrogens via what enzyme? What is the ER-alpha pathways in prostate? |
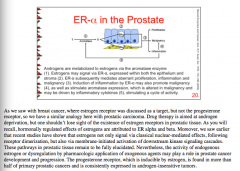
Estrogens signal ER-alpha => epithelium and stroma, ER-a mediates proliferation, inflammation, and malignancy => induction of inflammation by ER-alpha promotes malignancy => stimulates aromatase expression => cycle of activity |
|
|
What does ER-beta signaling do? |

Located and expressed within the glandular epithelium ER-beta => beneficial and protective, anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, and anti carcinogenic effects => decreased aromatase expression => reduced local estrogens |
|

|

|

