![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skin |
|
|
|
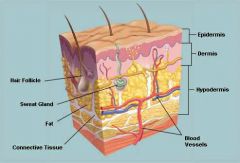
Skin |
The skin is a living functioning organ that plays a key role in maintaining the body's homeostasis
The skin protect the human body but it also allows humans to connect with the outside world
The skin is composed of two main layers the epidermis and the dermis and contains accessory organs such as sweat glands and hair follicles
The skin is a dynamic organ that functions in protection temperature regulation sensation excretion and absorption in the human body Burn damage to skin can impact numerous body functions and body systems in the human body
Both the body's ability to sense pain and to suppress pain and help protect the human body from injury and death |
|
|
Skin Vocabulary |
Collagen an insoluble fiber is protein of vertebrates that is the chef constituent of the fibrils of connective tissue is in skin and tendons and of the organic substance of bones Connective tissue Animal tissue that functions mainly to bind and support other tissues having a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular Matrix Dermis The sensitive vascular inner mesodermic layer of skin Elastin A protein that is similar to call again and as the chief constituent of elastic fibers Endorphin A hormone produced in the brain and anterior pituitary that inhibits pain perception Epidermis The outer non-sensitive and non vascular layer of the skin of a vertebrate that overlies the dermis A membranous cellular tissue that covers a free surface or lines a tube or cavity of an animal body and service especially to enclose and protect the other parts of the body to produce secretions and excretions and to function in assimulation Exocrine gland Epithelium A membranous cellular tissue that covers a free surface or lines a tube or cavity of an animal body and service especially to enclose and protect the other parts of the body to produce secretions and excretions and to function in assimulationExocrine gland A gland is a sweat gland and salivary Glendora kid need that releases a secretion external to or at the surface of an organ by means of a canal or ductFirst degree burn A mild burn characterized by feet pain and reddening of the burn surface but not exhibiting blistering or jarring of tissuesKeratin A gland is a sweat gland and salivary Glendora kid need that releases a secretion external to or at the surface of an organ by means of a canal or duct First degree burn A mild burn characterized by feet pain and reddening of the burn surface but not exhibiting blistering or jarring of tissues Any of various sulfur-containing fibrous proteins that form the chemical basis of epidermal tissues as hair and nails and are typically not digested by enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract Melanin Any of various black dark brown reddish brown or yellow pigments of animal or plant structure (as in skin and hair) Pain Basic bodily sensation that is induced by a noxious stimulus is received by naked nerve endings is characterized by physical discomfort (as pricking dropping are aching) and typically into evasive action Sebaceous gland Any of the small sacculated glands lost in the substance of the dermis usually opening into the hair follicles and secreting an oily or greasy material composed and great part of that which softens and lubricates the hair and skin Second-degree burn Auburn marked by pain blistering and superficial destruction of dermis with edema and no hyperemia of the tissues beneath the burn Third-degree burn Severe burn characterized by destruction of the skin to the depth of the dermis and possibly into underlying tissue loss of fluid and sometimes shock |
|
|
Burns |

|
|
|
Burns |
|
|
|
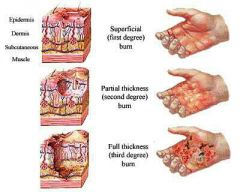
Burns |
First degree burns may be treated with skin care products like aloe vera cream or antibiotic ointment and pain medication such as acetaminophen Tylenol
Second-degree burns may be treated with an antibiotic cream or other creams or ointments prescribed by a doctor
The treatment of third-degree Burns may require the process of skin grafting or the use of synthetic skin severe burns covering large parts of the body may need more intensive treatment such as IV antibiotics to prevent infection in IV fluids to replace fluids lost when skin was burned |
|
|
Bone |
|
|
|
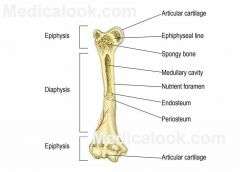
Bone Vocabulary |
Bone marrow A soft highly vascular modified connective tissue that occupies the cavities and cancel is part of most bones and occurs in two forms yellow and red
Bone remodeling The continuous turnover of bone matrix and mineral that involves first an increase in resorption and osteoclast activity and later reactive bone formation by osteoblast activity Calcitonin A poly peptide hormone especially from the thyroid gland the fens to lower the level of calcium in the blood plasma Callus A growth of new bone tissue in and around a fractured area ultimately replaced by mature bone Cartilage Usually a translucent somewhat elastic tissue that composes most of the skeleton of vertebrates embryos and except for a small number of structures as some joints respiratory passages and the external ear is replaced by bone during ossification and the higher vertebrates
Compact bone Bone tissue that contains few spaces between osteons forms the external portion of all bones and the bulk of the diaphysis shaft of long bones Diaphysis The shaft of a long bone
Epiphysis The end of a long bone usually larger in diameter than the shaft
Fracture The breaking of hard tissue (as bone)
Osteoblast A bone forming cell Osteoclast Any of the large multinucleated cells closely associated with areas of bone resorption as in a fracture that is healing
Osteocyte Cell that is characteristic of adult bone is isolated in a lacuna of the bone substance Cell that is characteristic of adult bone is isolated in a lacuna of the bone substance
Parathyroid hormone A hormone of the parathyroid gland that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body
Spongy (cancellous) bone Bone tissue that consists of an irregular latticework of thin plates of bone called trabeculae found inside short, flat, and irregular bones and in the epiphysis of a long bone |
|
|
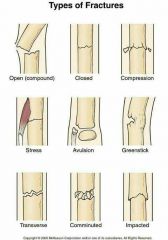
Different Types of Breaks |
|
|
|
4 Stages of Bone Healing |
Step 1 Hematoma Formation Blood vessels that are rupture during the breaks well to form a mass called hematoma this nass forms between the broken bones
Step 2 Fibrocartilage Callus Formation New capillaries begin to form into the clotted blood in the damaged area. connective tissue cells form a mass of repair tissue called a fibrocartilage callus. this callous contains some cartlidge some bone and collagen fibers and the combined mass closes the gap between the broken bones
Step 3 Bony Callus Formation The fibrocartilage callus is gradually replaced by one made of spongy bone this new mass is referred to as the Bony callus osteoclast and osteoblast moved to the area and multiply
Step 4 Bone Remodeling Over the weeks and months to come the callus is remodeled with the help of osteoclast and osteoblast the shape of the bones will gradually return to normal and there will eventually be little evidence of the fracture |
|
|
Calcium Feedback Loop |
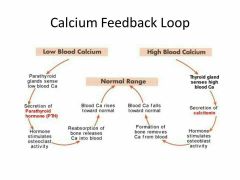
|
|
|
Lymph and Blood Cells |

|
|
|
Lymphatic System |
Consist of organs ducts and nodes and transports a watery clear fluid called lymph Lymph vessels interact with the circulatory system to drain the fluid from your cells and tissues Lymph also distributes immune cells around the body anything that is foreign to the body and get your immune system fired up is referred to as an antigen. antibody is are proteins and blood and lymph that seek out and bind to specific antigens. these specialized proteins are one of the primary defenders and your body's army of immunity your body contains tons of antibodies is designed to target and destroy specific antigen |
|
|
Blood Transfusions |

|

