![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
herpetic whitlow
|
HSV infection od igits; often children, dental and medical personnel who dont use gloves
|
|
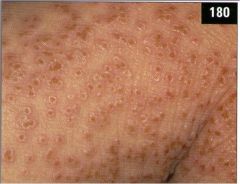
|
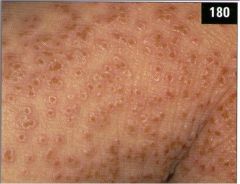
ezcema herpeticum (rare but svere disseminated herpes infection at sites of skin damage); occurs in pts with atopic dermatitis; distinct umbilication o fthe lesions
|
|
|
dsDNA -> enveloped -> icosahedral -> linear
|
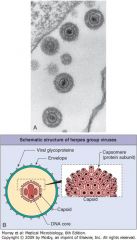
herpesvirus
|
|
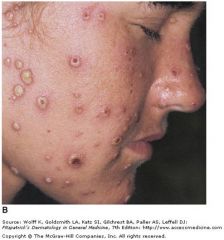
Began on face and scalp and spreads RAPIDLY to trunk with SPARING OF EXTREMITIES; "dew-drop on a rose petal lesions"
|
varicella; herpes family (dsDNA, icosahderal, enveloped, linear)
|
|
|
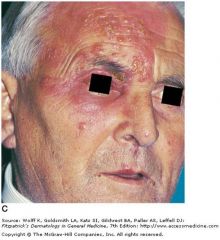
opthalmic zoster; herpes family (dsDNA -> enveloped -> icosahderal -> linear)
opthalmic zoster = invlvement of opthalmic nerve/eye indicated by lesion on tip of the nose pain is major symptom; can persist after rash has healed (postherpetic neuralgia) |
|
|
Dumbell shaped core
|
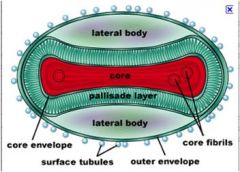
Pox viruses; dsDNA -> enveloped -> Complex = Pox Cirus
|
|
|
Guarnieri inclusion bodies and uncoatase
|
Guarineria inclusion bodies and uncoatase (removes core membrane) diagnostic for poxvirus
|
|
|
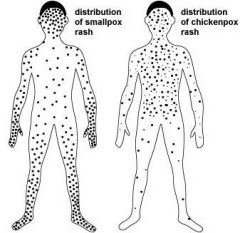
Distribution of smallpox vs chickenpox rash
|
|
|
|
centripedal rash
|
chickenpox; face and trunk
|
|
|
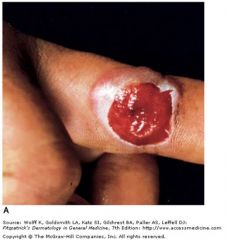
milkers nodule; parapoxviridae or pseudocowpox; transmission in the skin from infected animals or fresh meat; localized dz in healthy individuals
poxvirus; dsDNA -> enveloped -> complex shape |
|
|
Prarie dogs
|
Monkey pox; Poxvirus family
dsDNA -> enveloped -> complex |
|
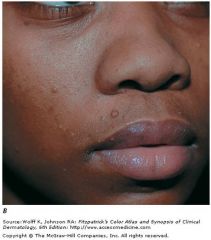
|
Molluscum contagiosum lesions; resolves spontaneously after 6m in healthy people; without aggressive therapy in HIV/AIDS pts regression does not occur
|
|
|
H protein
|
Hemagglutinin protein in measles which serves as attachment protein
ssRNA -> negative sense -> enveloped -> helical = paramyovirus |
|
|
ssRNA -> negative sense -> enveloped -> helical = paramyovirus
|
Paramyxoviridae family = measles (koplik spots)
|
|
|
Measles receptor
|
CD46 on all nucleated cells and SLAM (CD150) on T and B cells; transmitted by respiratory droplets; targets epithelial cells of the upper respiraotry tract
|
|
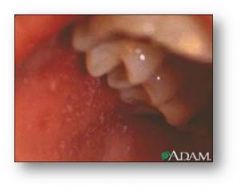
|
Koplik spots of measles inside the mouth;
|
|
|
ssRNA -> positive sense -> enveloped -> icosahderal
|
Togaviridae; Rubiella virus
only one of the togaviridae with a tight shrink wrapped like appearance |
|
|
blueberry muffin baby
|
ssRNA -> positive -> enveloped -> icosahedral = togaviridae = rubella virus
bone marrow dysfunction leads to extramedullary hematopoiesis |
|
|
High grade fever vs low grade fever in rubella vs measles
|
Measles = high grade fever
Rubella = low grade fever |
|
|
ssDNA -> naked -> icosahedral -
|
Parvovirus B19 (fifths dz or acute aseptic arthritis in adults)
erythrocyte P antigen receptor |
|
|
aseptic (viral) meningitis
|
ssRNA -> positive -> Naked -> icosahedral = Picronavirus -> enterovirus
also associated w herpangina (coxsackie A) |
|
|
ssRNA -> positive -> Naked -> icosahedral =
|
Picornavirus = enteroviruses (fecal oral transmission); consider aseptic meningitis
|
|
|
roseola
|
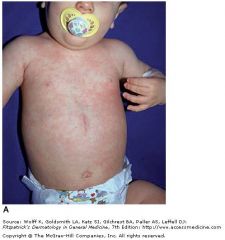
human herpesvirus 6; sixth disease or exanthema subitum
dsDNA -> enveloped -> icosahedral -> linear -> herpesvirus Exanthem subitum in an infant showing truncal pink macules and some papules that appeared 1 day after defervescence. |
|
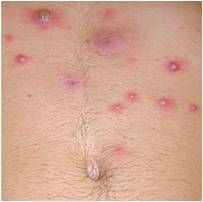
|
furunculosis are large painful, raised nodules that have an underlying collection of dead and necrotic tissue.
|
|
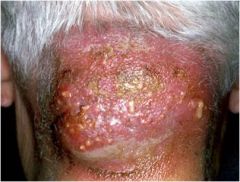
|
Carbuncles occur when furuncle coalesce and ext to the deeper subcutaneous tissue and is often associated with system spread via bacteremia causing fevers and chills; caused by s. aureus
|
|
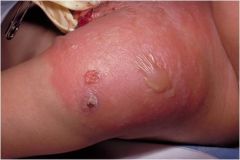
|
is a common infection of the skin and the soft tissues underneath the skin. Bacteria invade broken or normal skin and start to spread under the skin and into the soft tissues.
Inflammation may cause swelling, redness, pain, and/or warmth; caused by staph |
|
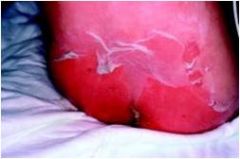
|
also known as Ritter von Ritterschein disease (in newborns), Ritter disease, and staphylococcal epidermal necrolysis, encompasses a spectrum of superficial blistering skin disorders caused by the exfoliative toxins of some strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Severity of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome varies from a few blisters localized to the site of infection to a severe exfoliation affecting almost the entire body
|
|
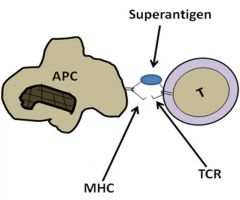
which staph toxins act as superantigens
|
exfoliative toxin A and TSST-1
SAg binds TCR and MHC II simultaneously; nonspcific stimulatoin of T cells; cytokin estorm; hypotension, shock, fever |
|
|
alpha toxin
|
Lyses cells by creating pores disrupting muscle tissue, blood vessels, lyses erythrocytes, hepatocytes and platelets.
|
|
|
beta toxin
|
Catalyses the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin and lysophosphatidylcholine as a result it disrupts membranes and cause lysis.
|
|
|
Delta toxin
|
It acts as a surfactant to disrupt membranes.
|
|
|
Gamma and P-V leukocidin:
|
Both are composed of 2 peptide chains. They lyse leukocytes and macrophages
|
|
|
P-V leukocidin
|
a pore forming toxin. It is rare in hospital acquired MRSA Staphylococcus aureus infections but is found in 100% of community acquired MRSA Staph aureus infection. This reflects the current understanding that the evolution of MRSA in these two contexts occurred independently. One did not originate with the other.
Actually P-V producing S. aureus appears to be associated with community acquired Furunculosis (boils) or severe hemorrhagic pneumonia or both found in young adults and children. The important connection being that young adults suffering from recurrent boils and presenting with pneumonia deserves particular attention because the mortality rate associated with the hemorrhagic lung disease is very high. |
|
|
exfoliative toxins
|
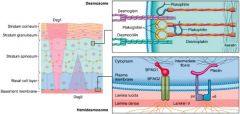
Exfoliative toxins are serine proteases that split desmoglein, which is one of a series of proteins required for holding cells together in the stratum granulosum of keratinized epidermis. As a result there is severe blistering and then exfoliation. The degree of exfoliation depends on the degree of dissemination.
|
|
|
staphylokinase
|
dissolves clots
|
|
|
lipase
|
allows for survival in sebaceous areas o fthe body
|
|
|
Dnase
|
hydrolyzes abscess material reducing viscosity so that the bacterial cell does not get trapped and eliminated.
|
|
|
coagulase
|
The cell bound form clumps Staphylococcal cells and the secreted form converts fibrinogen to fibrin to cause formation of a fibrin layer around the Staphylococci and causes clot formation. The protects the bacterial cells from phagocytosis.
|
|
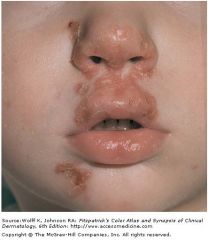
Golden-yellow crusts
|
Impetigo; s. aureus; crusted erosions lasting days to weeks; usually children
|
|
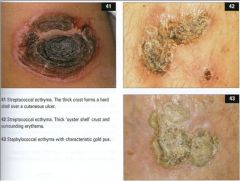
Ecthyma
|
thicker oyster shell like crust; s. aureus infection of epidermis extending into dermis (lesion of neglect)
|
|
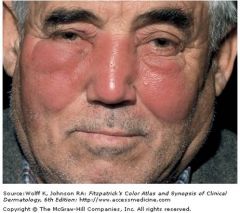
Painful, well-defined, shiny, erythematous, edematous plaques involving the central face of an otherwise healthy male. On palpation the skin is hot and tender.
|
Erysipelas; GAS; Acute, spreading infections of dermal and subcutaneous tissues
A red, hot, tender area of skin Often originating at the site of bacterial entry |
|
|
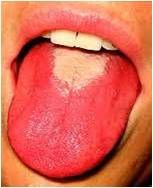
strawberry tongue of scarlet fever; usually GAS
occurs after pharyngitis GAs produces streptolysins O and s, antibodies to anti-streptolysin O can be used to assess recent GAS infection |
|
|
Necrotizing fasciitis localized to the scrotum and perineal area that spreads up the abdominal wall
|
Fournier's gangrene
NF caused by s. pyogenes; rapidly progressing infection involving subcutaneous tissue and fascia |
|
|
hot tub folliculitis
|
pseudomonas
|
|
|
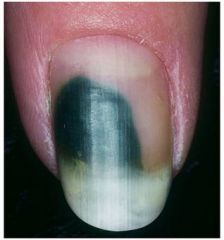
Green nail; produced by pseudomonas; cutaneous infections in healthy persons
pseudomonas also produces oht tub folliculitis |
|
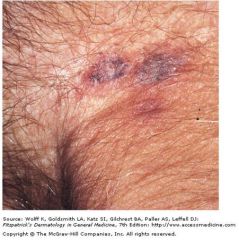
gunmetal gray, painless, infarcted lesions with surroudning erythema
|
ecthyma gangrenosum
|
|
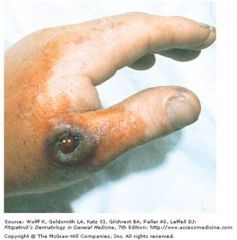
|
classic cutaneous anthrax lesion; painless papule that evolves into a hemorrhagic bulla with surrounding nonpitting edema
aerobic, spore forming gram positive rod, nondemolytic with an irregular border |
|
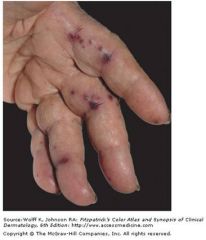
Janeway lesions indicate what (black spots on hands and feet)
= hemorrhagic, infarcted papules |
infective endocarditis
|
|
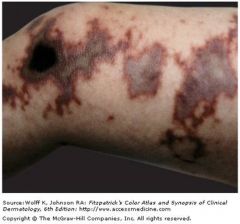
Maplike, gray-to-black areas of cutaneous infarction of the leg in a child with NM meningitis and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
|
acute meningococcemia purpura fulminans
|
|
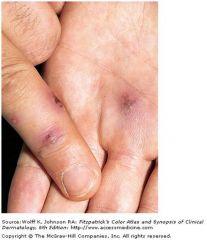
|
Disseminated gonococcal infection Hemorrhagic, painful pustules on erythematous bases on the palm and the finger of the other hand = sin manifestations of disseminated gonococcal infection
|
|
|
Gram-negative enteric bacillus, motile, facultative anaerobe, non-lactose fermenting, H2S producer.
|
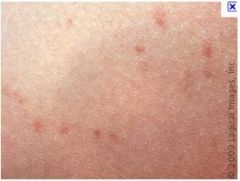
salmonella typhi: Presentation: fever, malaise, headache, constipation, rose spots (rash)
|
|
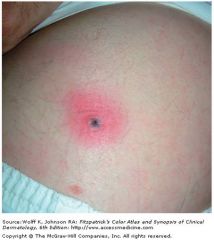
Rash on trunk -> extremities
|
tick borne typhus;
|

