![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functionally describe joints and give an example of each |
- synarthroses: non-movable e.g. sutures of the skull - amphiarthroses (cartilagenous): slightly moveable e.g. pubic symphysis - diarthrotic (synovial): freely moveable e.g. knee |
|
|
Structurally describe joints and give an example of each |
- fibrous:generally synarthrotic joints. no joint cavity and held together by connective tissue e.g. skull suture cartilagenous: amphiarthrotic joints. no synovial cavity and the bones are held together by hyaline or fibrocartilage e.g. pubic symphysis - synovial joints: diarthrotic. Contain syovial cavity and have articular cartilage e.g. knee |
|
|
What are the three types of fibrous joint? |
sutures (skull) gomphoses (teeth) syndesmoses (between long bones) |
|
|
What are the two types of cartilagenous joint? |
- synchondroses: made of hyaline cartilage and synarthrotic. Found in the epiphyseal plate of long bones in children. - symphyses: amphiarthrotic joints covered in hyaline cartilage with fibrocartilage in-between. Located along the midline: intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis. |
|
|
Draw a synovial joint |
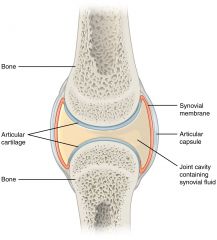
|
|
|
List the different types of synovial joint and give an example of each (6) |
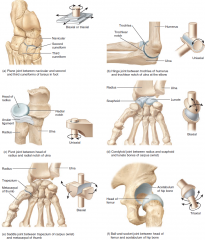
|
|
|
Describe the 3 types of movement at synovial joints |
- uniaxial: one plane of motion - biaxial: two planes of motion - multiaxial: multiple axes |
|
|
Describe bursa and tendon sheaths |
bursa: fluid-filled sacs which absorb pressure and reduce friction in joints tendon sheaths: tube-like bursae that wrap around tendons. Protects tendon from friction. |
|
|
What are the 5 functions of articular discs/menisci? |
- shock absorption - improve "fit" between articulating bones - provide adaptable surfaces for combined movements - increase surface area for weight distribution - distribute synovial fluid over articulating surfaces |

