![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some external features unique to chickens?
|
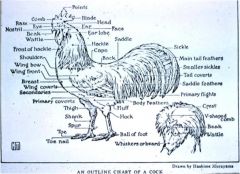
Comb, wattle, metatarsal spurs, saddle feathers
|
|
|
What does it mean if the saddle feathers of a chicken are round or pointy?
|
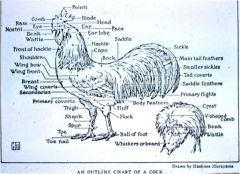
Point = male
Round = female |
|
|
Why is it important to know about external nares in birds?
|
They can get infections there - especially macaws.
|
|
|
Do all chickens have wattles?
|
No - some breeds don't have them.
|
|
|
Do raptors have wattles?
|
No - that's just a chicken thing.
|
|

What's hanging off the front of these turkeys? What about off of their face above the beak?
|

The beard and the snood, respectively.
|
|
|
What's the point of the snood?
|

Displays of manly turkeyness.
Meow |
|
|
what part of a raptor can you scratch like you'd scratch a dog head that they just love?
Are chickens the same? |
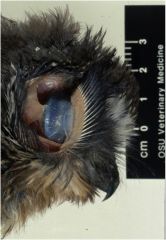
Their external acoustic meatus.
You won't see this in chickens |
|
|
What groupings of flight feathers are there?
|

Primaries - coming from the "hand"
Secondaries - coming from the radius and ulna. Alula used for guidance. |
|
|
What is unique about avian ulnas?
|

They are longer than the radius and the secondary feathers actually insert into them.
|
|
|
What's the center part of the flight feather called? What parts make it up?
|
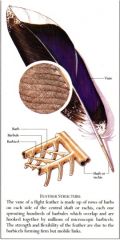
The shaft - made up of the rachis (the main shaft) and the calamus (the quill).
|
|
|
What are the feather parts of the flight feather called? What are the subunits of this part?
|
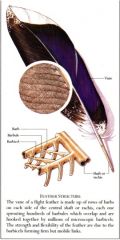
The vane - made up of barbs, barbules, and hooklets (barbicels in the picture)
|
|
|
T/F hooklets in flight feathers are arranged in all directions.
|
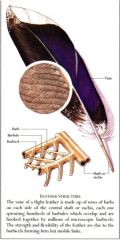
False - the hooklets are all aligned to make the vane smooth and orderly.
|
|

How can you tell the sex of this bird?
|

The pointy saddle feathers and the metatarsal spur tell you it's a male.
|
|
|
Do birds have third eyelids?
|

Yes
|
|
|
What do you call the feathered and featherless areas of birds?
|
Pterylae and Apterylae respectively.
|
|

What is siginifigant about the apterylae of this young macaw?
|

This shows you where there will be no feathers...and there won't be feathers there.
|
|
|
How have avian bones been altered to make birds capable of flight?
|
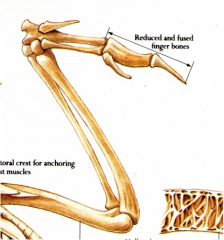
They have pneumatic bones - hollow femurs and humeruses.
Their fingers bones are reduced and fused - have very few to drop the weight. |
|
|
Where do the major flight muscles originate from?
|
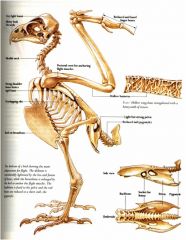
The keel.
|
|
|
In birds, what bones join at the scapulo-humeral joint?
|
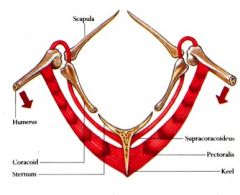
Scapula, humerus, coracoid
|
|
|
What hole does the supracoracoideus tendon go through in the bird?
|
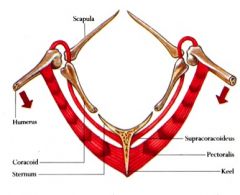
The foramen trioseum
|
|
|
What muscles are responsible for a bird down stroke?
|
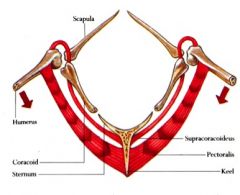
Pectoralis m.
|
|
|
What muscle is responsible for the up stroke of bird wings?
|

The supracoracoideus m.
|
|
|
what are the modifications mentioned for enabling birds for flight?
|
Light skull bones
Strong pectoral girdle Reduced digits Alula Large keel and crest on humerus for flight muscles Hollow bones Shortened tail Fused vertebrae |
|
|
What is the gliding to powerstroke ratio of albatross and penguins/hummingbirds? What about raptors and ducks/chickens/geese?
|
20:1 and 2:1 for albatross and penguins/hummingbirds.
10:1 and 5:1 for raptors and ducks/chickens/geese Clinically important for knowing what to expect when necropsying. The supracoracoideus m and pectoralis mm. will be various stages of equal/unequal dependent on this. |
|
|
what is the function of the scleral ossicles?
|
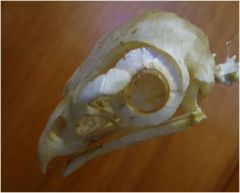
Shortening and lengthening the entire eyeball for heightened vision.
|
|
|
What is a unique feature of some birds (like the macaw) maxilla?
|
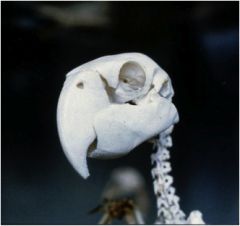
It's hinged.
|
|
|
what is the bone unique to the bird skull allowing the mandible to open?
|
The quadrate bone.
|
|
|
What type of energy metabolism is used in white muscle?
|
Anaerobic metabolism.
|
|
|
What gives aerobic muscle the dark color?
|
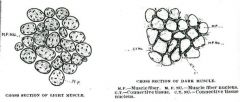
The mitochondria.
Dark meat also has more capillaries due to the higher metabolic needs. |
|
|
What is the histological differences of white meat?
|
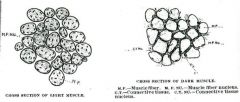
Big fibers, fewer vessels, few mitochondria
|
|
|
What does the pectineus m. insert in in brids?
|

The tendon of the digital flexor tendon. This means that when the leg is flexed, the feet are gripping - important for perching and for grabbing prey - draw prey up toward them.
|
|
|
What is the infundibulum in birds?
|
There are two infundibulum in the bird:
The opening to the paranasal sinuses. And the place where the yolk sac gets a covering of albumen before moving on to the magnum. |
|
|
What are the internal nares in birds called?
|
The choana
|
|
|
Does the glottis hang out open or closed?
|
Closed except for inspiration.
|
|
|
What is the mesobronchus?
|
The primary bronchi in the lungs.
|
|
|
What do you have coming off of primary bronchi?
|
Secondary bronchi, then tertiary bronchi (or parabronchi), then atria, then air capillaries
|
|
|
Do birds have peritoneal or pleural cavities?
|
no.
|
|
Where would the tertiary bronchi be here?
|
You can see the secondary bronchi coming off of the primary bronchi. The tertiary bronchi would connect the secondary like ladder rungs.
|
|
|
Do air sacs have respiratory function?
|
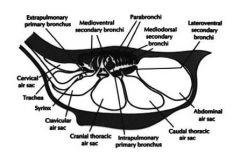
No - they act only as bellows.
|
|
|
How do birds breathe?
|
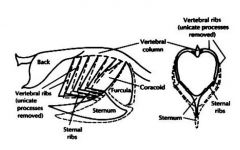
Keel moves away from the spine - inspiration (inflates the bellows). Moves back toward the spine - expiration.
This is why you don't grab birds and restrain them by squeezing the thorax. |
|
|
how many inspiration/expirations does it take air to get back out of the avian lung? Trace that pathway.
|
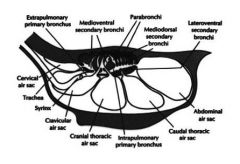
Two - first inspiration it gets back to the caudal air sac. First expiration it moves into the lung. The second inspiration, it moves into the cranial air sacs, then on the second expiration it moves out. This allows for continuous fresh air flow across the lungs.
|
|
|
Which is larger, the right or left jugular a. of the chicken?
|
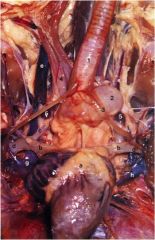
The right larger. (e)
|
|
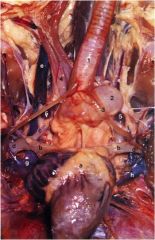
What are 2., 3., and 5.?
|
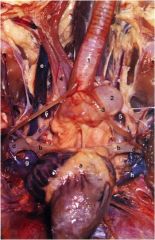
2 - the syrinx
3 - the sternotrachealis m. 5 - the thyroid gland |
|
|
What is the major blood supply to the limb in the bird?
|
The ishiatic artery.
|
|
|
What is the renal portal system of the bird?
|
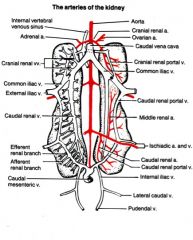
Capillaries in legs that then go on to the kidneys - point: don't give injections in the legs.
Ext. iliac vein (coming in just above caudal renal portal v. on the right) comes in and goes through a valve that is closed under parasympathetic stimulation, and open under sympathetic. |
|
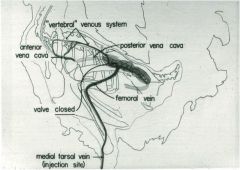
Here's a picture of the renal portal valve closed in birds.
|
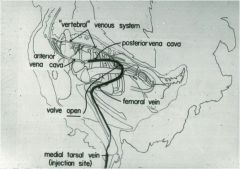
And here it is open.
|
|
|
What are the pieces to the bird GI tract?
|
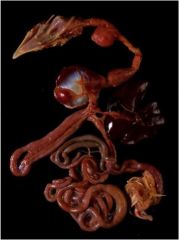
beak, crop, esophagus, proventriculus, gizzard (ventriculus), duodenum, 2 ceca, colon, cloaca
|
|
What is the stuff at the left shoulder of this normal duck?
|
Gravel in the gizzard.
|
|
cover up the right of this picture and ID this stuff.
|
good.
|
|
|
How many oviducts do birds have?
|
One
|
|
|
Where does the albumen get added to the ovum in the bird?
Where does the shell membrane get added? Where does the shell get added? |
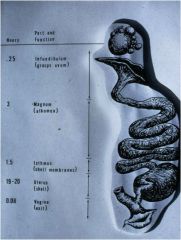
The magnum, isthmus and uterus, respectively.
|
|
|
Where does the vagina open into the bird?
|
The urodeum
|
|
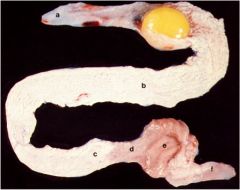
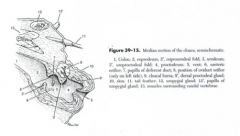
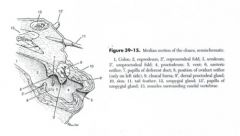
ID these parts of the female bird reproductive tract
|
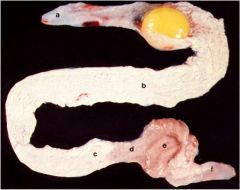
a - infundibulum
b - magnum c - isthmus d - shell gland f - vagina |
|
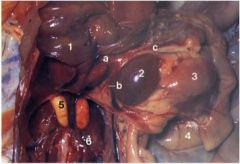
What are 2 and 5 here?
|
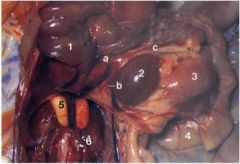
2 - spleen
5 - immature testes. |
|
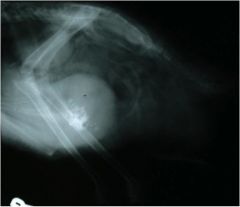
Can you see the testes of this bird?
|
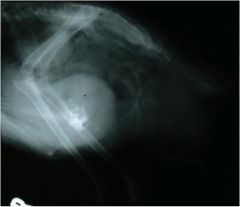
They are seen between the humeruses......if those are humeruses.
|
|

What type of muscle is the iris in birds?
What's the clinical siginifigance of this? |

It's skeletal muscle. So atropine won't work on dilating bird eyes. And they use the irises to "flash" - which is an aggressive warning.
|

