![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
For postmenopausal cysts, what size and characteristics is it that require surgery? |
> 5 cm and those containing internal septations, and / or solid nodules |
|
|
What are some common cystic or complex ovarian mass? |
Follicular cyst, corpus luteum cyst of pregnancy, cystic Teratoma, paraovarian cyst, hydrosalpinx, endometrioma, hemorrhagic cyst. |
|
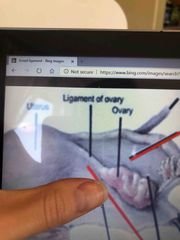
The first red arrow (courses through the broad ligament):
The black arrow (adjacent to left ovary)
The last red arrow: |
1. Mesometrium 2. Mesovarium 3. Mesosalpinx |
|
|
What are common complex ovarian masses? |
Cystadenoma (benign) when malignant, Cystadenocarcinoma Dermoid cyst Tubo- ovarian abscess Ectopic pregnancy Granulosa cell tumor |
|
|
This occurs third, fourth decade of life. Arises from broad ligament. These are wolffian duct remnants. Pt is asymptomatic. Can extend into upper abdomen is it gets large enough. |
Paraovarian cyst |
|
|
This predominantly occurs in premenopausal women with hx of abdominal surgery. Pelvic pain, adhesions present. Fluid around ovaries (large adnexa mass) |
Peritoneal inclusion cyst. |
|
|
Solid tumors, most common? |
Serous types: Cystadenoma, cystadenocarcinoma. Malignancy for fertile years vs after age 40. Fertile years 1 in 15 malignant, 1 in 3 after age 40. |
|
|
Differential for a solid appearing adnexal mass include? |
Dermoid, thecoma, granulosa cell tumor, fibroma, pedunculated fibroid, brenner tumor, mets. |
|
|
What are common solid masses in ovaries? |
Fibroma, torsion, solid Teratoma, adenocarcinoma, arrhenoblastoma, dysgerminoma. |
|
|
What are common solid masses in ovaries? |
Fibroma, torsion, solid Teratoma, adenocarcinoma, arrhenoblastoma, dysgerminoma. |
|
|
Regarding the indices and diastolic flow, what is the appearance in the first 7 days to later in the cycle? Know the cycle for your patient to determine diastolic flow increase is false or malignant, how? |
First 7 days; Greatest resistance with lowest diastolic flow- indices at highest. Later in cycle- diastolic flow increases in dominant ovary. Lower indices. Increased diastolic flow suggest neovascularity and malignancy. Could be false if in beginning of cycle. |
|
|
What are common solid masses in ovaries? |
Fibroma, torsion, solid Teratoma, adenocarcinoma, arrhenoblastoma, dysgerminoma. |
|
|
Regarding the indices and diastolic flow, what is the appearance in the first 7 days to later in the cycle? Know the cycle for your patient to determine diastolic flow increase is false or malignant, how? |
First 7 days; Greatest resistance with lowest diastolic flow- indices at highest. Later in cycle- diastolic flow increases in dominant ovary. Lower indices. Increased diastolic flow suggest neovascularity and malignancy. |
|
|
If a mass of showing complete absence of diastolic flow or minimal but RI and PI is elevated, this means it’s usually benign or malignant? |
Benign. |
|
|
Functional cyst include? |
Corpus luteum, follicular cyst, hemorrhagic, theca lutein cyst. Theca lutein cyst associated with abnormal pregnancy. |
|
|
This finding in the ovaries follows FAWDE, it’s about 7cm, pt is experiencing asymptomatic to dull, adnexal pressure and pain. Abnormal ovarian function. Finding? |
Follicular cyst. |
|
|
What are theca lutein cyst? |
Abnormal pregnancy. Bilateral multi loculated cysts associated with high levels of hCG. Seen 30% of pt with trophoblastic disease. |
|
|
What are theca lutein cyst? |
Abnormal pregnancy. Bilateral multi loculated cysts associated with high levels of hCG. Seen 30% of pt with trophoblastic disease. |
|
|
Preg Pt has nausea / vomiting. Multiloculated cysts in both ovaries are large. Finding? |
Theca lutein cyst. |
|
|
What are theca lutein cyst? |
Abnormal pregnancy. Bilateral multi loculated cysts associated with high levels of hCG. Seen 30% of pt with trophoblastic disease. |
|
|
Preg Pt has nausea / vomiting. Multiloculated cysts in both ovaries are large. Finding? |
Theca lutein cyst. |
|
|
Ovaries are enlarged, <5 cm in diameter. Pt has pelvic discomfort. It’s a complication of ovulation induction. If severe it’s assoc with ascites, thin walled cyst throughout periphery of ovary. |
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. |
|
|
Pt is 28, Bilateral enlarged ovaries. Clinical: amenorrhea. Multiple tiny cyst on periphery of ovary.includes Stein-Leventhal syndrome. |
Polycystic ovarian syndrome. (String of Pearls). |
|
|
Pt is 28, Bilateral enlarged ovaries. Clinical: amenorrhea. Multiple tiny cyst on periphery of ovary.includes Stein-Leventhal syndrome. |
Polycystic ovarian syndrome. (String of Pearls). |
|
|
Urachal and omental cysts tend to be high / low throughout the abdomen? These cyst are 4.5 times more common than omentalcysts? |
Omental cysts- higher in abdomen. (Located in the lesser or greater omentum) Urachal cysts- midline in anterior abdominal wall. Mesenteric cysts than omentalcysts. |
|
|
What is this: functioning endometrial tissue is present outside the uterus? |
Endometriosis |
|
|
Pt has chronic pelvic pain. Known as a chocolate cyst, bilateral or can be unilateral. Range from Anechoic to solid. This is diffuse and appearance is similar to PID or chronic ectopic pregnancy. Finding? |
Endometriosis |
|
|
This finding is well defined in the ovary. Mainly cystic, diffusely homogenous, low level internal echoes. |
Endometrioma |
|
|
This finding is well defined in the ovary. Mainly cystic, diffusely homogenous, low level internal echoes. |
Endometrioma |
|
|
Female Pt has been vomiting. Pale, fever, absent blood flow in ovaries. Free fluid in pelvis. Associated with a mass. Hypoechoic enlarged ovary with or without peripheral follicles. |
Ovarian torsion. |
|
|
This finding is well defined in the ovary. Mainly cystic, diffusely homogenous, low level internal echoes. |
Endometrioma |
|
|
Female Pt has been vomiting. Pale, fever, absent blood flow in ovaries. Free fluid in pelvis. Associated with a mass. Hypoechoic enlarged ovary with or without peripheral follicles. |
Ovarian torsion. |
|
|
Which ovary is three times more likely to torse? |
Right ovary |
|
|
In postmenopausal women ovaries size? Abnormal ovaries suggestive for malignancy are defined by what characteristics? |
Atrophy unless on hormonal replacement therapy. Then normal sized ovaries. Enlarged, echogenic ovaries. |
|
|
In postmenopausal women ovaries size? Abnormal ovaries suggestive for malignancy are defined by what characteristics? |
Atrophy unless on hormonal replacement therapy. Then normal sized ovaries. Enlarged, echogenic ovaries. |
|
|
What cancer kills more female between 40-60 years old. It’s known as the fourth leading cause of cancer death? |
Ovarian carcinoma. Kills more than uterine cervix and body combined. |
|
|
Ovarian masses <__ or >__ are more likely to be benign or malignant? |
<5 cm benign >10 cm malignant |
|
|
Incidence is higher for women to get ovarian cancer if? |
Who have had breast cancer or colon cancer. |
|
|
Women with carcinoma of the breast have increased their risk to developing? |
Ovarian carcinoma 3-4 times more likely. |
|
|
Women with carcinoma of the breast have increased their risk to developing? |
Ovarian carcinoma 3-4 times more likely. |
|
|
Pt complains of indigestion, constipation, bloating, weight gain, ascites. This is called? |
Ovarian carcinoma |
|
|
Women with carcinoma of the breast have increased their risk to developing? |
Ovarian carcinoma 3-4 times more likely. |
|
|
Pt complains of indigestion, constipation, bloating, weight gain, ascites. This is called? |
Ovarian carcinoma |
|
|
Cancer classified into stages; explain? |
Stage 1- limited to ovaries, ascites. Stage 2- limited to pelvis Stage 3- limited to abdomen- intrabdominal extension outside pelvis, retroperitoneal nodes Stage IV- Hematogenous disease (liver parenchyma) spread beyond abdomen. |
|
|
For epithelial tumors most common are? |
Serous and mucinous Tumors. Serous- most common, comprise of all 30% ovarian neoplasm. Mucinous Tumors: 20-25% of ovarian neoplasm. |
|
|
Difference between serous and mucinous? |
Serous- smaller, higher % to become malignant, unilocular and effect bilateral ovaries. Mucinous- Large, smaller % to being benign, multilocular, effect unilateral ovary. |
|
|
Most common benign tumor of ovaries? |
Mucinous cystadenoma. When malignant cystadenocarcinoma. |
|
|
Clinical- big belly, pain. This is usually found in woman between age 13-45. Finding very large measuring 15-30 cm diameter unilateral. Appears Simple cyst, multilocular. Considered a choc cyst. Finding? |
Mucinous cystadenoma |
|
|
This finding in the ovary most frequently occurs in women 40-70 years old. If this ruptured, assoc with pseudomyxoma peritoneum. Causes loculated ascites. Cyst appears thick, irregular wall, septations, echogenic material. Finding? |
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma |
|
|
What’s the second most common benign tumor of the ovary? |
Serous cystadenoma |
|
|
Clinical: pelvic fullness, bloating. Cystic structure with septations / papillary projections, internal and external papilloma present. Loss of capsular definition, calcifications. |
Serous Cystadenocarcinoma. |
|
|
Nearly all this type of tumors are malignant. Approx 20-30% bilateral, most frequently occurs with postmenopausal, peak age range 50-60 years old. |
Endometrioid tumor (Epithelial tumor) |
|
|
Endometrioid tumor is associated with? |
Endometriosis |
|
|
These are considered rare tumors, incidental finding in a pelvic exam. |
Brenner tumor (Transitional cell tumor) |
|
|
These are considered rare tumors, incidental finding in a pelvic exam. |
Brenner tumor (Transitional cell tumor) |
|
|
This tumor is associated with elevated with AFP and hCG levels. Pt has pelvic / abdominal pain. Unilateral. Predominant solid. |
Germ cell tumors |
|
|
These are considered rare tumors, incidental finding in a pelvic exam. |
Brenner tumor (Transitional cell tumor) |
|
|
This tumor is associated with elevated with AFP and hCG levels. Pt has pelvic / abdominal pain. Unilateral. Predominant solid. |
Germ cell tumors |
|
|
What are germ cell tumors? |
Dysgerminoma, embryonal cell carcinoma, choriocarcinoma, endodermal sinus tumor. |
|
|
Tip of iceberg refers to? |
Dermoid tumor |
|
|
This finding occurs in girls to young women 10-20 yo. Mrapidly growing, solid malignant tumor with many tiny cyst. Unilateral and small in size. |
Immature and mature Teratoma. |
|
|
What tumors are most common ovarian neoplasm seen in pregnancy? |
Dysgerminoma and serous cystadenoma |
|
|
Entire solid ovarian mass in women in less than 30 yo usually have what kind of tumor? |
Dysgerminoma (germ cell tumor) |
|
|
This tumor occurs in women under 20 yo. Unilateral ovary, AFP elevated. It’s the second most common malignant ovarian germ cell neoplasm Yolk sac tumor can be in scrotal also. |
Endodermal sinus tumor. |
|
|
Metastatic tumor of the ovary from the Gi tract, “headlight sign.” |
Krukenberg tumor |
|
|
Sex cord stromal tumors include? |
Granulosa cell tumor, thecoma, fibroma, sertoli-leydig cell tumor. |
|
|
Sex cord stronal tumors include? |
Granulosa cell tumor, thecoma, fibroma, sertoli-leydig cell tumor. |
|
|
Thecoma and fibroma; difference? |
Thecoma - abundance of theca cells. Shows signs of estrogen production. Fibroma- abundance of fibrous tissue. Rarely assoc with estrogen production. |
|
|
Sex cord stronal tumors include? |
Granulosa cell tumor, thecoma, fibroma, sertoli-leydig cell tumor. |
|
|
Thecoma and fibroma; difference? |
Thecoma - abundance of theca cells. Shows signs of estrogen production. Fibroma- abundance of fibrous tissue. Rarely assoc with estrogen production. |
|
|
Found in post menopausal women, assoc with ascites along with pleural effusion. Unilateral on ovaries. Hypoechoic mass with posterior attenuation. Referred to as Meigs syndrome. Called? |
Fibroma |
|
|
Sex cord stronal tumors include? |
Granulosa cell tumor, thecoma, fibroma, sertoli-leydig cell tumor. |
|
|
Thecoma and fibroma; difference? |
Thecoma - abundance of theca cells. Shows signs of estrogen production. Fibroma- abundance of fibrous tissue. Rarely assoc with estrogen production. |
|
|
Found in post menopausal women, assoc with ascites along with pleural effusion. Unilateral on ovaries. Hypoechoic mass with posterior attenuation. Referred to as Meigs syndrome. Called? |
Fibroma |
|
|
This includes in estrogen production may include precocious puberty or vaginal bleeding. Most common hormone active estrogen ic tumor of ovary. |
More common after menopause 50%. Reproductive age 45% Adolescence 5% |
|
|
Mets disease, krukenberg tumor is metastases to ovaries from? |
Gi tract, primarily from stomach, but also biliary tract, gallbladder, pancreas. |
|
|
Carcinoma of Fallopian tube usually involve? |
Distal end. May involve entire length of tube. Least common. Occurs most frequently in postmenopausal women sigh pain, vag bleed, pelvic mass. |
|
|
What is rokitansky nodule? |
Dermoid plug |
|
|
What are other potential pelvic masses? |
Ectopic pregnancy, pelvic kidneys, omental / mesentery cyst, diverticulum abscess, retroperitoneal masses, distended bladder. Colon cancer or mass. |
|
|
What is adenomyosis? |
Diffuse, uterine enlargement, bully uterus, thickening or posterior myometrium, myometrial cysts. Sono sign: Venetian blind |
|
|
Ovarian volume in menstruating can be as large of a volume as? |
22 cc highest. Between 5-15 cc for menstruating females. |
|
|
To find the ovarian measurement? |
0.523 x length x width x height |
|
|
What stimulates luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone? |
Pituitary gland. |
|
|
What matured following ovulation in luteal phase? |
Corpus luteum matures and is identified as hypoechoic or isoechoic structure peripherally in the ovary. Ring color Doppler around the isoechoic corpus luteum. If no pregnancy, corpus luteum undergoes hemorrhaging or collapsing within itself post ovulating 8 or 9 days or with onset of menstruation. |
|
|
Suspect potential malignancy with ovary Doppler if? |
Intratumoral vessels, low resistance flow, absence of normal diastolic notch |
|
|
What are the equations for RI, PI for ovary Doppler? |
RI: (PSV-EDV) / PSV; cutoff value is 0.4. PI: (PSV- EDV) / Mean velocity; cutoff value is 1.0 Benign disease would be above these values and malignant would be below these values. |
|
|
What are the equations for RI, PI for ovary Doppler? |
RI: (PSV-EDV) / PSV; cutoff value is 0.4. PI: (PSV- EDV) / Mean velocity; cutoff value is 1.0 Benign disease would be above these values and malignant would be below these values. |
|
|
What’s the largest part of the uterus? |
Corpus |
|
|
What are the equations for RI, PI for ovary Doppler? |
RI: (PSV-EDV) / PSV; cutoff value is 0.4. PI: (PSV- EDV) / Mean velocity; cutoff value is 1.0 Benign disease would be above these values and malignant would be below these values. |
|
|
What’s the largest part of the uterus? |
Corpus |
|
|
Distal portion containing the cornua housing portion of Fallopian tube? |
Fundus |
|
|
When conceptus implants what induces decidualization of the endometrium? |
Corpus luteum secreting progesterone (conceptus implanted in endometrium produces hCG, how it signals corpus luteum to keep producing. |
|
|
What are the phases on the ovarian cycle? |
Follicular, ovulatory, Luteal |
|
|
What are the phases on the ovarian cycle? |
Follicular, ovulatory, Luteal |
|
|
Follicular phase ranges from what days? What occurs in this phase? |
1-14. Multiple follicles develop in both ovaries. Eventually a single follicle matures and becomes the grafiian follicle (Dominant follicle). The follicles 3-30 respond to FSH during each cycle. Maximum diameter between 15-30 mm. |
|
|
What day is ovulation? What occurs in this phase? |
Day 14. Occurs 10-12 hours after LH peak. Extrusion of a dominant follicle releasing oocyte and small amount of follicular fluid in peritoneal cavity. Follicular size decreases, fluid in posterior cul de sac, hemorrhage of dominant follicle. |
|
|
What day is ovulation? What occurs in this phase? |
Day 14. Occurs 10-12 hours after LH peak. Extrusion of a dominant follicle releasing oocyte and small amount of follicular fluid in peritoneal cavity. Follicular size decreases, fluid in posterior cul de sac, hemorrhage of dominant follicle. |
|
|
What’s the luteal phase? |
After Day 14 Ovulation. A ruptured dominant follicle involutes into a corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces progesterone which maintain secretory endometrium. In the absence of bHCG, corpus luteum atrophies and by the end of luteal phase, it’s completely regressed. |
|
|
What day is ovulation? What occurs in this phase? |
Day 14. Occurs 10-12 hours after LH peak. Extrusion of a dominant follicle releasing oocyte and small amount of follicular fluid in peritoneal cavity. Follicular size decreases, fluid in posterior cul de sac, hemorrhage of dominant follicle. |
|
|
What’s the luteal phase? |
After Day 14 Ovulation. A ruptured dominant follicle involutes into a corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces progesterone which maintain secretory endometrium. In the absence of bHCG, corpus luteum atrophies and by the end of luteal phase, it’s completely regressed. |
|
|
BHCG is produced by? |
Trophoblastic tissue of a conceptus. |
|
|
What are the endometrium layers? |
Innermost- echogenic line. Middle- echogenic functionalism layer. Outermost (deepest): Hypoechoic, Basalis layer |
|
|
What are the endometrium layers? |
Innermost- echogenic line. Middle- echogenic functionalism layer. Outermost (deepest): Hypoechoic, Basalis layer |
|
|
What pelvic muscles are within the false pelvis? |
Iliacus and iliac fossa |
|
|
The pelvic muscles within the true pelvis is? |
Obturator internus, Piriformis, Coccygeus, Levator Ani. |
|
Front (Term) |
OI and LA |
|
|
This pelvic muscle in the true muscle is on the lateral wall? On the posterior wall? On the posterior floor? Middle and anterior floor? |
Obturator internus. Posterior: Piriformis Posterior floor: Coccygeus Levator Ani: Middle and anterior floor. |
|
? |
Psoas major and the iliac muscle. (Abdominopelvic muscles and false pelvis ) |
|
|
What marks the border of the true and false pelvis? |
Iliopsoas muscle |
|
Which muscle is this? |
Levator ani muscle |
|
|
If one of these muscle fail prolapse structures can occur? |
Levator ani muscle |
|
|
Levator ani muscle made up of? |
Group of 3, Iliococcygeus, pugococcygeus, puborectalis. |
|
|
Levator ani muscle made up of? |
Group of 3, Iliococcygeus, pugococcygeus, puborectalis. |
|
|
Organs of the female in true pelvis? False pelvis? |
Pelvic colon, rectum, bladder, uterus, ovaries, Fallopian tubes, vagina, suspensory ligament. False pelvis: sigmoid colon, ileum. |
|
|
What’s the most flexible portion of uterus and considered largest portion? |
Corpus and isthmus (attach fundus to the cervix). |
|
|
What’s the most flexible portion of uterus and considered largest portion? |
Corpus and isthmus (attach fundus to the cervix). |
|
|
Endometrium thickness based on the days of the cycle? |
1-5: thin < 1mm 6-9 days: 2 to 4 mm 10-13 days: 5-8 mm 14-28 days: 9-14 mm |
|
|
What’s the most flexible portion of uterus and considered largest portion? |
Corpus and isthmus (attach fundus to the cervix). |
|
|
Endometrium thickness based on the days of the cycle? |
1-5: thin < 1mm 6-9 days: 2 to 4 mm 10-13 days: 5-8 mm 14-28 days: 9-14 mm |
|
|
Uterine variants positioning include? |
AntevertedUterus toward anterior abd wall. anteflexed- bending of fundus toward abdominal wall. retroverted- tipping of uterus toward sacrum. retroflexed- bending of fundus toward rectum. Dextroflexed- flexed to the right. Dextroposition-displaced to the right. levoposition-displaced to the left Levoflexed- flexed to the left. Prolapse- dropping of uterus into vaginal canal. |
|
|
Short portion within the uterine wall? Longest most dilatable? |
Interstitial Ampulla. |
|
|
Connects the lateral portion of the ovary from the posterolateral wall of the pelvis? |
Suspensory ligament |
|
|
Connects the lateral portion of the ovary from the posterolateral wall of the pelvis? |
Suspensory ligament |
|
|
Suspends the posterior surface of the ovary to Fallopian tube? Suspends the medial portion of the ovary to the uterine cornua area of uterus? |
Broad ligament Ovarian ligament |
|
|
What are the main muscles of the true pelvis; make up the pelvic floor diaphragm? |
Levator Ani muscle, Coccygeus muscle, Piriformis muscle |
|
|
These run anterior to internal iliac arteries and posterior to the ovaries? |
Ureters |
|
|
This structure is posterior to urinary bladder and urethra, anterior to rectum and anus? |
Vagina |
|
|
Vagina length? |
9 cm length |
|
|
Arterial supply from vaginal and uterine arteries drain to? |
Internal iliac vein |
|
|
What ligaments hold the uterus anteverted position? |
Round ligament |
|
|
Uterine size for premenarchal? |
1.0 - 3.0 cm length 0.5 - 1.0 cm width |
|
|
Uterine size for premenarchal? |
1.0 - 3.0 cm length 0.5 - 1.0 cm width |
|
|
Menarchal uterine size? |
6.0 - 8.0 cm length 3.0 - 5.0 width |
|
|
Uterine size for premenarchal? |
1.0 - 3.0 cm length 0.5 - 1.0 cm width |
|
|
Menarchal uterine size? |
6.0 - 8.0 cm length 3.0 - 5.0 width |
|
|
Multiparity increases size by? |
1-2 cm |
|
|
Uterine size for premenarchal? |
1.0 - 3.0 cm length 0.5 - 1.0 cm width |
|
|
Menarchal uterine size? |
6.0 - 8.0 cm length 3.0 - 5.0 width |
|
|
Multiparity increases size by? |
1-2 cm |
|
|
Postmenopausal uterine length? |
3.5 to 5.5 cm length. 2.0-3.0 cm width |
|
|
What are the layers of the uterus? |
Perimetrium - Serous outer layer of uterus; serosa. Myometrium- muscular middle layer of uterus. Endometrium- inner mucous membrane. |
|
|
This uterine ligament is the upper fold of the broad ligament; encloses the Fallopian tube? |
Mesosalpinx |
|
|
This uterine ligament is the upper fold of the broad ligament; encloses the Fallopian tube? |
Mesosalpinx |
|
|
This uterine ligament is the posterior fold of broad ligament; encloses the ovary? |
Mesovarium |
|
|
This uterine ligament is the lateral aspect of the uterus to pelvic sidewalk? |
Broad ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament is the lateral aspect of the uterus to pelvic sidewall? |
Broad ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament is by the fundus to the anterior pelvic sidewalls; holds uterus forward. |
Round ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament extends across the pelvic floor laterally and supports the cervix? |
Cardinal ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament extends across the pelvic floor laterally and supports the cervix? |
Cardinal ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament extends from the uterine isthmus downward, along the side of the rectum to sacrum. Supports cervix. |
Uterosacral ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament extends across the pelvic floor laterally and supports the cervix? |
Cardinal ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament extends from the uterine isthmus downward, along the side of the rectum to sacrum. Supports cervix. |
Uterosacral ligament |
|
|
This uterine ligament extends from lateral aspect of ovary to pelvic sidewall? This uterine ligament extends medially from ovary to uterine cornua? |
Suspensory ligament. Ovarian ligament |
|
|
Follicles in ovaries secrete which hormone? |
Estrogen. |
|
|
Follicular development and ovulation is regulated by? |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
Follicular development and ovulation is regulated by? |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
Follicular development and ovulation begins with hypothalamus which starts like? |
Gonadotropin releasing hormone. This stimulates anterior pituitary gland to secrete levels of gonadotropins. Primarily FSH and LH. |
|
|
Follicular development and ovulation is regulated by? |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
Follicular development and ovulation begins with hypothalamus which starts like? |
Gonadotropin releasing hormone. This stimulates anterior pituitary gland to secrete levels of gonadotropins. Primarily FSH and LH. |
|
|
What’s the phases for endometrium for the cycle? |
Early proliferative phase: thin endo, late proliferative phase: triple sign, ovulation, secretory phase. In proliferate endo thickens 4-8mm. Right before ovulation endometrium is 6-10 mm After ovulation, secretory phase: 7-14 mm |
|
|
Endometrium with postmenopausal on HRT versus non HRT? |
Not on HRT; endometrial thickness < 5mm. On HRT, normal endometrial thickness up to 8 mm. |
|
|
Amenorrhea means? Menorrhagia means? Dysmenorrhea means? |
Absent period. Abnormally long heavy periods. Painful periods. |
|
|
What is the space anterior to the fundus, between uterus and bladder? |
Vesicouterine pouch (anterior could de sac) |
|
|
What is the space anterior to the fundus, between uterus and bladder? |
Vesicouterine pouch (anterior could de sac) |
|
|
What’s the space between the uterus and rectum? |
Rectouterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas), posterior cul de sac. |
|
|
What is the space anterior to the fundus, between uterus and bladder? |
Vesicouterine pouch (anterior could de sac) |
|
|
What’s the space between the uterus and rectum? |
Rectouterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas), posterior cul de sac. |
|
|
The space of Retzius is? |
Between the bladder and symphysis pubis. |
|
|
What is the space anterior to the fundus, between uterus and bladder? |
Vesicouterine pouch (anterior could de sac) |
|
|
What’s the space between the uterus and rectum? |
Rectouterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas), posterior cul de sac. |
|
|
The space of Retzius is? |
Between the bladder and symphysis pubis. |
|
|
The posterior wall is formed by? |
Sacrum and coccyx |
|
|
What is the space anterior to the fundus, between uterus and bladder? |
Vesicouterine pouch (anterior could de sac) |
|
|
What’s the space between the uterus and rectum? |
Rectouterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas), posterior cul de sac. |
|
|
The space of Retzius is? |
Between the bladder and symphysis pubis. |
|
|
The posterior wall is formed by? |
Sacrum and coccyx |
|
|
Posterolateral wall is formed by which muscles to make the pelvic cavity? |
Piriformis muscle and Coccygeus muscle |
|
|
What’s the most common benign ovarian neoplasm? |
Cystic Teratoma |

