![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cardiac output The volume of blood pumped each minute by each ventricle |
Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate (ml/minute). (Ml/beat). (Beats/min) a. Average heart rate = 70 BPM b. Average stroke volume equals 70-80 ml/beat c. Average cardiac output equals 5,500 ml/minute |
|
|
Regulation of stroke volume |
Regulated by three variables a. And diastole volume (EDV): volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole *aka preload * Stroke volume increases with increased EDV b. Total peripheral resistance: frictional resistance in the arteries * Inversely related to stroke volume * aka afterload c. Contractility: strength of ventricular contraction stroke volume increases with contractility * Normally, about 60% of the EDV is ejected - ejection fraction |
|
|
What is the factors affecting the cardiac output? |
Stroke volume and heart rate |
|
|
What are the factors affecting the stroke volume |
Preload, afterload, contractility |
|
|
Net filtration pressure |
is the hydrostatic pressure of the blood in the capillaries minus the hydrostatic pressure of the fluid outside the capillaries. a. Hydrostatic pressure is 37 mmHg and at the venial and is 17 mmHg b. Hydrostatic pressure of interstitial fluid is 1 mmHg c. Net filtration pressure is 36 mmHg arterial end and 16 mmHg xenial end |
|
|
Colloid osmotic pressure |
a. Due to proteins dissolved in fluid b. blood plasma has higher osmotic pressure than interstitial fluid. This difference is called oncotic pressure. 1) oncotic pressure =25 mmHg 2) this favors the movement of fluid into the capillaries |
|
|
Starling forces |
Combo of hydrostatic pressure and oncotic pressure that predicts movement of fluid across capillary membranes Fluid movement is proportional to Pc= hydrostatic pressure in capillary πi= colloid osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid Pi= hydrostatic pressure of interstitial fluid πp= colloid osmotic pressure of blood plasma |
|
|
Edema |
a. Excessive accumulation of interstitial fluids b. May be the result of: *High atrial blood pressure *Venous obstruction *Leakage of plasma proteins into interstitial space *myxedema (excessive production of musen in extracellular spaces caused by hypothyroidism) *Decrease plasma protein concentration *Obstruction of lymphatic drainage |
|
|
Role of sympathetic nervous system |
a. Increase blood volume in the Atria stimulates stretch receptors that leads to increased sympathetic stimulation to the heart and decrease stimulation to the kidneys b. Kidney arterioles dilate, increasing blood flow and increases urine production that will decrease blood volume |
|
|
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin) |
a. produced by the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary when osmoreceptors detect ⬆️ plasma osmolality b. Plasma osmolarity can ⬆️ due to excessive salt intake or dehydration c. ⬆️ plasma osmolarity also ⬆️ thirst d. ADH stimulates water re-absorption e.⬆️ Water intake and ⬇️ urine formation ⬆️ blood volume f. Blood becomes dilute, and ADH is no longer released g. Stretch receptors in left atrium, carotid sinus, and aortic arch also inhibit ADH release h. stretch receptors in the Atria also stimulated the release of atrial natriuretic peptide which ⬆️ excretion of salt and water from kidneys to reduce blood volume |
|
|
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
BP⬇️=> Kidney cells (juxtaglomerular apparatus) secrete the enzyme renin a. Angiotensinogen => angiotensin 1 by renin b. Angiotensin 1 => angiotensin II by ACE enzyme c. Angiotensin II has many effects that result in a ⬆️ in BP Vasoconstriction of small arteries and arterioles to increase peripheral resistance Stimulates thirst center in hypothalamus Stimulates production of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex d. Can also work the opposite direction to reduce blood pressure |
|
|
Regulation by atrial natriuretic peptide |
a. Produced by the Atria of the heart when stretch is detected from high-volume or ⬆️ venous return b. promote salt and water excretion in urine in response to ⬆️ blood volume c. Inhibits ADH secretion d. Antagonist of aldosterone |
|
|
Blood pressure Affected by blood volume/ stroke volume, total peripheral resistance, and cardiac rate |
a. Increase in any of these will increase blood pressure b. Basal constriction of arterial leaves raise blood pressure upstream in the arteries c. Arterial blood= cardiac x total peripheral Pressure. Output. Resistance |
|
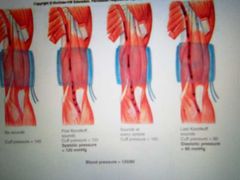
Blood pressure measurement |
Measured using sphygmomanometer Average BP is 120 systolic/80 diastolic |
|
|
The BP cuff produces turbulent flow in the brachial artery, which is heard by a stethoscope the sound is called? |
Sounds of Korotkoff |
|
|
Because is first inflated to beyond systolic Blood pressure to pinch off an artery. As pressure is released, the first sound is heard at ____________ and a reading can be taken. |
Systole |
|
|
The last Korotoff sound is heard when the pressure in the cuff reaches __________ pressure and a second reading can be taken. |
Diastolic |
|
|
Mean arterial pressure |
*Average pressure in the arteries in one cardiac cycle is the mean arterial pressure (MAP) *Significant because the difference between map and venous pressure that drives the blood into the capillaries. Calculated as Diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure Pp= systolic - diastolic |
|
|
Hypertension |
Increasing in age Risk of cardiac diseases, kidney diseases and stroke Essential =primary or secondary |
|
|
Types of congestive failure (CHF) |
a. Left side failure raises left arterial pressure and produces pulmonary congestion and edema causing shortness of breath b. right side failure raises right arterial pressure and produces systemic congestion and edema |

