![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define O2 partial pressure, O2 content & %Hb saturation?
|
O2 partial pressure is the total absolute pressure X volume fraction of gas component
O2 content is the mass of O2 per unit volume (ml O2 / dl blood) %Hb saturation is the fraction of O2 binding sites that are actually occupied |
|
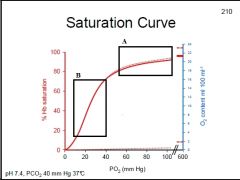
What does the dotted line represent?
What does Box A represent? What does Box B represent? |
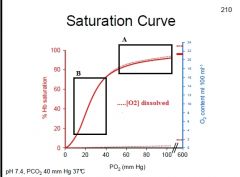
Box A: "Plateau" is loading of O2, even good if alveolar PO2 falls slightly, keeping blood well saturated w/ O2
Box B: Steep region is offloading of O2 at tissues, a slight change in PO2 significantly affects unloading of O2 from Hb |
|
|
Define P(50)?
|
The [O2] needed for 50% binding
|
|
|
An ↑P(50) affects binding & affinity how?
A ↓P(50) affects binding & affinity how? A ↓pH affects binding & affinity how? |
↑P(50) means a lot of PO2 is needed for 50% binding, thus ↓affinity & easier to offload
↓P(50) means little PO2 is needed for 50% binding, thus ↑affinity & low O2 to bind ↓pH means low affinity and thus offloading |
|
|
How would the following conditions affect the O2 - Hb saturation curve:
↑Temp? ↑pH? ↑CO2? ↑2,3-DPG? |
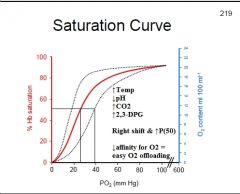
↑Temp: Rt. shift of curve
↑pH: Lt. shift of curve ↑CO2: Rt. shift of curve ↑2,3-DPG: Rt. shift of curve |
|
|
How will Hb concentration, O2 content, Hb saturation, Hb binding sites & O2 carrying capacity of blood be affected in a patient w/ polycythemia?
|
Polycythemia:
↑Hb concentration ↑O2 content 100% Hb saturation ↑Hb binding sites ↑O2 carrying capacity of blood |
|
|
How will Hb concentration, O2 content, Hb saturation, Hb binding sites & O2 carrying capacity of blood be affected in a patient w/ anemia?
|
Anemia:
↓Hb concentration ↓O2 content 100% Hb saturation ↓Hb binding sites ↓O2 carrying capacity of blood |
|
|
How will the O2-Hb saturation curve be changed w/ an anemic patient?
How will O2 saturation be affected? |
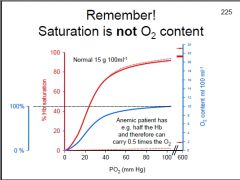
Rt. shift & down of curve
O2 saturation will still be 100% |
|
|
How is the O2-Hb saturation curve affected by CO poisoning?
How is O2 saturation affected? |
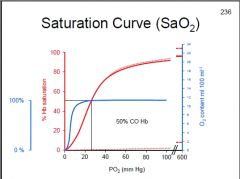
Lt. shift and down
O2 saturation is still 100% |
|
|
What are the (5) forms that CO2 is carried in the blood?
What is the major one and its fraction in arterial blood? |
Dissolved CO2
Carbonic acid Bicarbonate Carbonate Carbamino compounds Bicarbonate is the major form found in the blood, accounting for 90%. |
|
|
How would CO2 transport be affected by a decrease of Cl- available to RBC's?
|
CO2 is taken up by RBC's and converted to HCO3- + H+ in the presence of carbonic anhydrase. HCO3- is transported out of the cell by a Cl- cotransporter. A decrease in Cl- would slow this transporter, HCO3- would accumulate in the RBC & CO2 would not be taken up by the RBC
|
|
|
How would CO2 transport be affected by a decrease of Cl- available to RBC's?
|
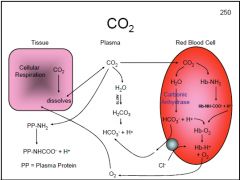
CO2 is taken up by RBC's and converted to HCO3- + H+ in the presence of carbonic anhydrase. HCO3- is transported out of the cell by a Cl- cotransporter. A decrease in Cl- would slow this transporter, HCO3- would accumulate in the RBC & CO2 would not be taken up by the RBC
|
|
|
What does the Bohr Effect tell us about CO2 and O2?
What does the Haldane Effect tell us about CO2 and O2? |
Bohr Effect: ↑PCO2 will ↓O2 carrying capacity
Haldane Effect: ↑PO2 will ↓CO2 carrying capacity |
|
|
During respiratory acidosis how is PCO2, pH & HCO3- affected?
|
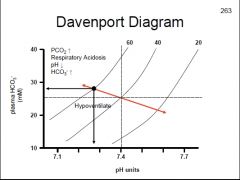
↓pH, ↑HCO3-, ↑PCO2
|
|
|
During respiratory alkalosis how is PCO2, pH & HCO3- affected?
|
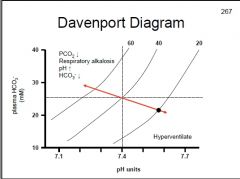
↑pH, ↓HCO3-, ↓PCO2
|
|
|
How does the body compensate for respiratory alkalosis?
|
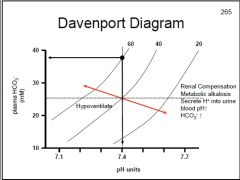
Metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
How does the body compensate for respiratory acidosis?
|
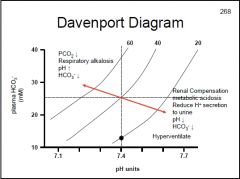
Metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
For the following, would a respiratory alkalosis or acidosis occur:
High altitude? V/Q mismatch? ↑Alveolar ventilation? ↓Lung diffusing capacity? ↓Alveolar ventilation? Anxiety? Aspirin intoxication? Hypoventilation? COPD? Hyperventilation? |
High altitude: resp. alkalosis
V/Q mismatch: resp. acidosis ↑Alveolar ventilation: resp. alkalosis ↓Lung diffusing capacity: resp. acidosis ↓Alveolar ventilation: resp. acidosis Anxiety: resp. alkalosis Aspirin intoxication: resp. alkalosis Hypoventilation: resp. acidosis COPD: resp. acidosis Hyperventilation: resp. alkalosis |
|
|
A patient has:
pH: 7.25 HCO3-: 28 mM PCO2: 60 mm Hg A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
A) Respiratory acidosis
|
|
|
A patient has:
pH: 7.3 HCO3-: 18 mM PCO2: 40 mm Hg A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
B) Metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
A patient has:
pH: 7.6 HCO3-: 22 mM PCO2: 20 mm Hg A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
C) Respiratory alkalosis
|
|
|
A patient has:
pH: 7.5 HCO3-: 35 mM PCO2: 40 mm Hg A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
D) Metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
Patient has:
↓pH, ↑HCO3-, ↑PCO2 A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
A) Respiratory acidosis
|
|
|
Patient has:
↑pH, ↑HCO3-, no change in PCO2 A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
D) Metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
Patient has:
↓pH, ↓HCO3-, no change in PCO2 A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
B) Metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
Patient has:
↑pH, ↓HCO3-, ↓PCO2 A) Respiratory acidosis B) Metabolic acidosis C) Respiratory alkalosis D) Metabolic alkalosis |
C) Respiratory alkalosis
|

