![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What nerve supplies the central portion of the diaphragmatic pleura and mediastinal pleura
|
Phrenic Nerve
|
|
|
What nerves supply the costal and peripheral portions of the diaphragmatic pleura
|
Intercostal nerves
|
|
|
Two branches of what nerve innervates all muscles of the larynx and carries sensory fibers from the laryngeal mucosa?
|
Vagus nerve;
Reccurent laryngeal (all muscles except cricothyroid) and superior laryngeal (cricothyroid) |
|
|
Which branch of the vagus nerve innervates all muscles of the larynx except for the cricothyroid and provides sensory innervation of the laryngeal mucosa BELOW the vocal folds?
|
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
|
|
|
Which branch of the vagus nerve, through its external and internal branches), provides innervation to the cricothyroid muscle?
|
Superior Laryngeal Nerve;
External branch of SLN innervates the cricothyroid muscle and sends fibers to supply the inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx The internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve provides sensory innervation of the laryngeal mucosa ABOVE the vocal folds |
|
|
What does the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve supply
|
sensory innervation of the laryngeal mucosa ABOVE the vocal folds
|
|
|
What does the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve supply?
|
Innervates the cricothyroid muscle and sends fibers to supply the inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx
|
|
|
A pt presents with speech that is hoarse and weak. What nerve was severed?
|
Vagus nerve; lesions here result in paralysis of the vocal cord musculature;
|
|
|
Lesions of the superior laryngeal nerve present how
|
Largely asymptomatic, because its fibers are mainly sensory; if the motor fibers to the cricothyroid are affected in the external branch, there may be some mild hoarseness and a slight decrease in vocal strength
|
|
|
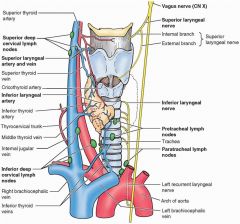
Which nerves are susceptible to injury in surgical procedures involving the thyroid gland?
|
Both reccurent laryngeal nerves; lesions here result in fixed vocal cord and transient hoarseness
|
|
|
Which side of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is found only in the neck?
|
Right
|
|
|
Which side of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is injured more often?
|
The left recurrent larngeal because it takes a longer course through the superior mediastinum and the neck
|
|
|
How would damage to the tractus solitarius affect breathing
|
Responsible for generation of respiratory rhythm and mainly inspiration;
|
|
|
Which brain area is hypothesized to be the location of the central respiratory rhythm generator circuitry
|
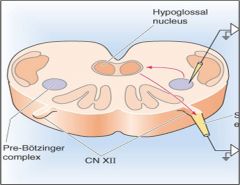
The pre-Boetzinger complex
|
|
|
Cheyne Stokes and heart failure
|
Delay of delivery of blood to brain, so brains control of breathing is always outdated about current levels of C02 in the blood; effects breathing in a crescendo/decrecrendo pattern
|
|
|
Which condition is more common in pts with rostral ventral lateral medulla lesions?
|
Sleep apnea
|
|
|
Conditions which can produce hypercapnia
|
pulmonary disease, emphysema, muscle weakness,
|
|
|
Function of Yawning
|
Yawning may minimize atelactasis (collapse of part o fthe lung) as one prepares for sleep; it's basically an exaggerated sigh
|
|
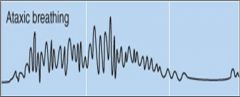
Damage where would produce ataxic breathing (disordered depth, timing and rate of respiration)
|
Pontomedullary damage; particularly the medulla
|
|
Damage where would produce ataxic breathing (disordered depth, timing and rate of respiration)
|
Pontomedullary damage; particularly the medulla
|
|
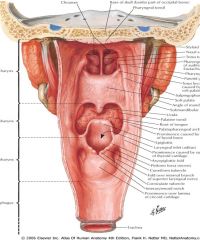
|
Pharynx; posterior view
|
|
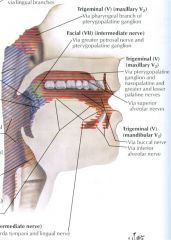
|
sensory innervatoin of the oral cavity
|
|
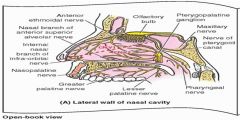
|
Innervation of the nasal cavity
|
|
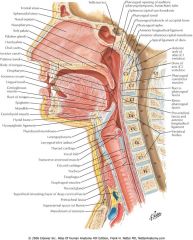
|
Pharynx; lateral view
|
|
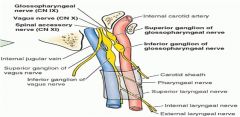
|
Vagus Ganglia
|
|
|
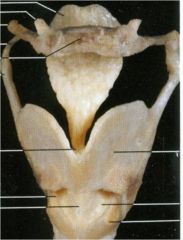
Cartilages of the larynx; locate the epiglottis, thyroid and cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
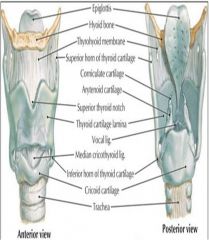
Larynx; note the epiglottis and thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
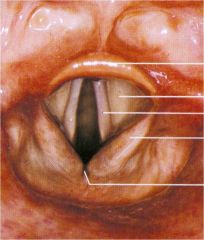
Larynx seen from above
Note two valleuclae, tip of the epiglottis, vestibular fold (false vocal) and vocal fold (true vocal) space between folds = rima glottidis |
|
|
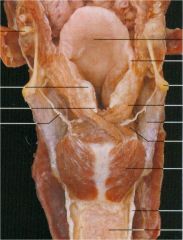
Posterior view of larynx
|
|
|
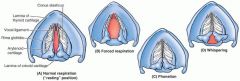
Movement of the vocal cords
|
|
|
Intrinsic muscles of the larynx
|
|
|
What is the only abductor of the vocal cords?
|
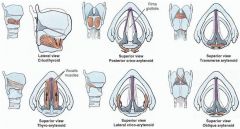
Posterior cricoarytenoid
Cricothyroid and thyroarytenoid tense cords Lateral cricoarytenoid adducts cords |
|
|
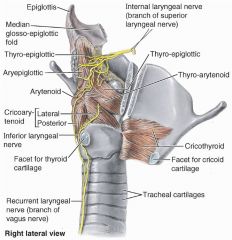
Course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve; since it passes arch of aorta, aortic pathology can produce hoarseness which can gradually get worse
|
|
|
Sole function of the superior laryngeal nerve of the vagus
|
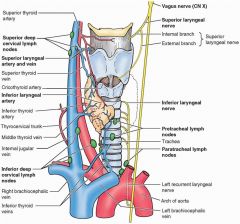
Innervate the cricothyroid muscle
everything else innervated by recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
|
Pt with montonous voice that tires easily
|
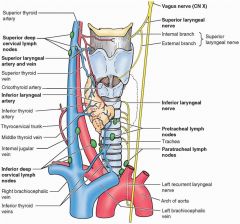
Paralysis of the external laryngeal nerve
|
|
|
Loss of sensation in the vestibule and larynx above the vocal fold
|
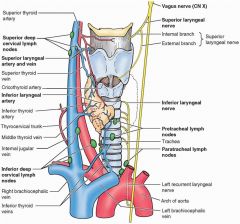
Paralysis of external laryngeal nerve
|
|
|
Loss of sensation to the larynx below the vocal cords; innervation of all intrinsic muscles of the larynx; paralysis causes hoarsenss and difficulty speaking
|
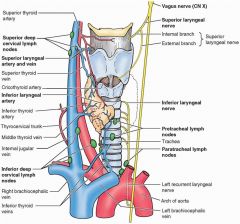
Paralysis of the recurrent laryngeal nerve; innervates muscles from below after running along the tracheoesophageal groove
|
|
|
Which ribs rotate around an axis during breathing?
|
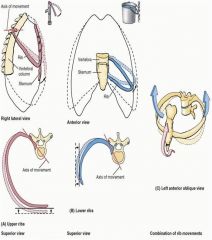
Upper ribs
|
|
|
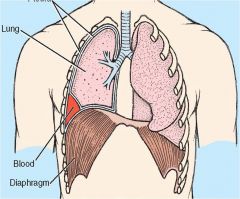
Hemothorax following stab wounds or fractured ribs; note blood in pleural space
|
|
|
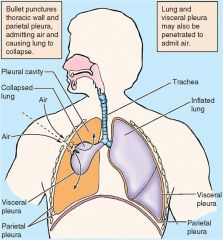
Pneumothorax collapses lung
|
|
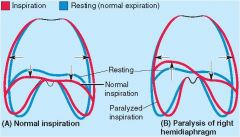
Paralysis of which nerve might cause paradoxical motion of the hemidiaphragm
|
Damage to the right phrenic nerve
|

