![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the main risk factor for community acquired pneumonia in adults?
|
Cigarette smoking
|
|
|
Pulmonary Clearance
|
Microorganisms not atken up by mucociliary escalator are killed by pulmonary alveolar macrophages, last line of defense. This process, called pulmonary clearance, is impaired by viral respiratory infections, tobacco smoke, chronic lung disease, alcohol, and many other factors associated with debilitating diseases
|
|
|
Purulent, rust colored, red streaked sputum
|
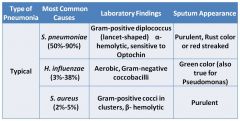
|
|
|
Green colored sputum
|
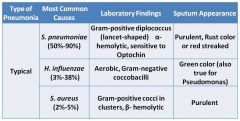
|
|
|
Off white/yellow sputum
|
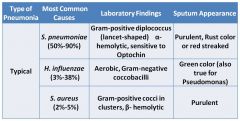
|
|
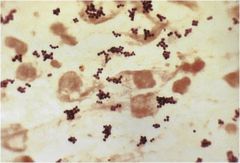
|
Staphylococcus aureus; sputum smear
|
|
|
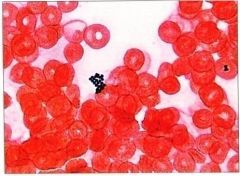
Staphylococcus aureus; blood smear
|
|
|
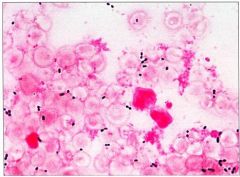
Streptococcus pneumoniae; blood smear
|
|
|
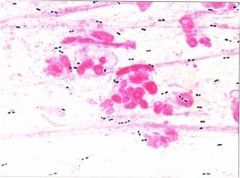
Streptococcus pneumoniae; sputum smear
Note mucus strands and neutrophils |
|
|
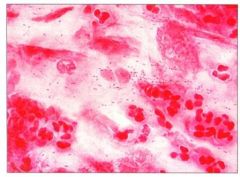
Haemophilus influenzae; sputum smear
Note neutrophils |
|
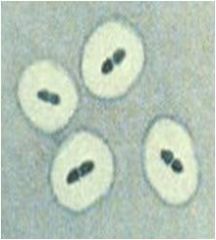
|
Positive Quellung reaction for streptococcus pneumoniae
|
|

This organism also has an IgA protease
|
H. influenzae; gram negative short rods; V factor requirement; grows on chocolate agar; satellite phenomenon
|
|
|
Organism known for causing pneumonia in chronic alcoholics and nosocomical pneomonia
|
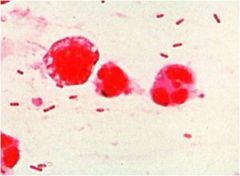
Klebisella pneumoniae
|
|
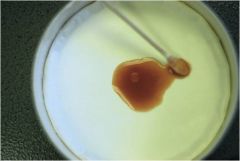
|
Currant jelly sputum associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia
|
|
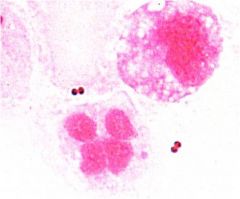
Moraxella catarrhallis
|
Rare pathogen in older adults with COPD
Gram negative diplococci Differentiated from Neisseria by its lack of carbohydrate fermentation |
|
|
Scant or watery sputum; which type of atypical pneominia should you suspect
|
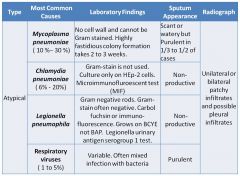
|
|
|
What is the major differentiating feature of atypical pneumonia?
|
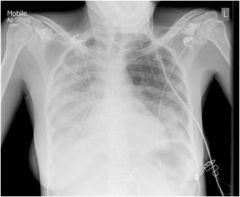
Unproductive cough
Symptoms progress from upper to lower respiratory tract often starting w sore throat Radiographs show much greater pulmonary involvement then normal |
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
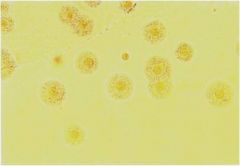
Most common cause of atypical pneumonia
Has no cell wall (so can't gram stain) Virulence factor: P1 adhesion and ciliostasis Fried egg appearance |
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
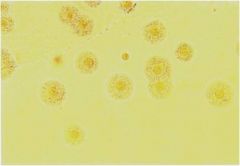
Most common cause of atypical pneumonia
Has no cell wall (so can't gram stain) Virulence factor: P1 adhesion and ciliostasis Fried egg appearance |
|
|
Legionella Pneumophilia
|

Rapid progression of disease and high fever (104) is characteristic
Grows on BCYE agar but not on media without L-cysteine (blood agar) |
|
|
What organism is an emerging cause of hospital acquired pneominiae which has developed substantial antimicrobial resistance
|
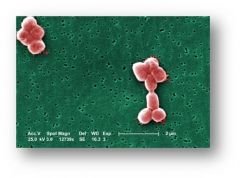
Acinetobacter
Gram negative, nonmotile rods, aerobic |
|
|
Fruity smelling sputum; most common gram negative bacterium found in nosocmial infections
|
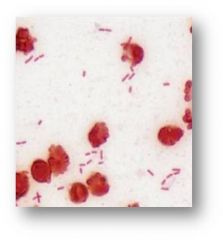
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram negative rods in pairs and singles |
|
|
Fruity smelling sputum; most common gram negative bacterium found in nosocmial infections
|
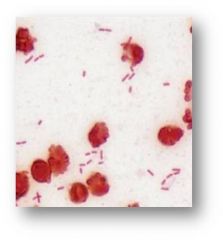
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram negative rods in pairs and singles |

