![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
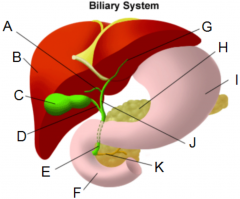
How many lobes and segments does the liver have? |
- 4 lobes 8 segments |
|
|
What are the main arterie(s) and vein(s) supplying the liver an what do they provide? |
- right and left hepatic arteries (oxygenated blood) - portal vein (absorbed nutrients) |
|
|
Describe the role of Kupffer cells in the liver (3) |
- phagocytic cell - forms the lining of the sinusoids of the liver - involved in the breakdown of red blood cells. |
|
|
What 3 veins unite to the form the portal vein? Where is blood in the portal vein transported from? |
- superior and inferior mesenteric veins and splenic vein - small intestine |
|
|
List 7 function of the liver |
- waste removal - breakdown of drugs - synthesis of clotting factors - bile production - storage of vitamins and minerals - glycogen storage and regulation - acute phase proteins |
|
|
What causes cirrhosis? Give 4 specific causes |
- chronic inflammation followed by scarring - drugs/toxins, congenital disorders, alcohol and viruses |
|
|
Give 9 signs and symptoms of cirrhosis? |
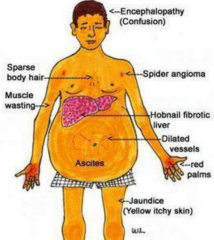
- |
|
|
What are ascites? What causes it? |
- oedema in the abdomen - portal hypertension |
|
|
|
|
|
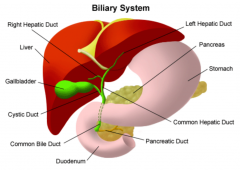
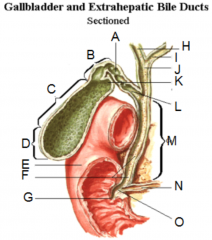
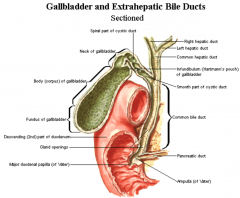
What is the funciton of the gall bladder? Which hormone is responsible for inducing this funciton? |
- storage and secretion of bile - cholecystokinin |
|
|
Which cell type lines the mucosa of the gall bladder? |
- simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
Whcih arteries and veins supply the gall bladder? Whcih nerves supply the gall bladder? |
- cystic artery and cystic veins - vagus (X) and splanchnic |
|
|
Give 5 non- modifiable risk factors for gall stones |
- family history - genetics - ethnicity - female gender - increasing age |
|
|
Give 5 modifiable risk factors for gall stones |
- obesity - sedentary lifestyle - diet - rapid weight loss - certain drugs e.g. thiazide diuretics and demale sex hormones |
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
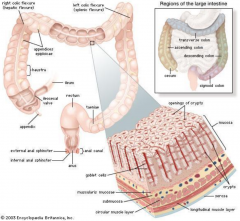
Give 7 fuctions of the liver |
- motility (e.g. haustral contractions) - absorption of water - mucous production - production of vit. K - breakdown of fibre - storage and elimanation of waste |
|
|
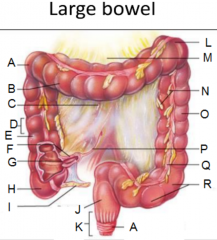
Give 6 causes of bowel obstruction |
- adhesions - malignancy - hermias - inflammatory bowel disease - volvulus (twist or turn in the intestine ( or stomach)) - impacted faeces - pseudo-obstruction (e.g. surgery, disrupted muscle/nerve coordination meds etc) |
|
|
Ulcerative colitis affects which parts of the GI? |
- large intestine - caecum to rectum |
|
|
Which age groups are most likley to present with ulcerative colitis? |
- 2 spikes of presentation - adolescents and young adults and middle aged people |
|
|
What part of the GI tract does Crohn's disease affect? Which tissue layers are affected? |
- anywhere from mouth to anus - all (transmural) |

